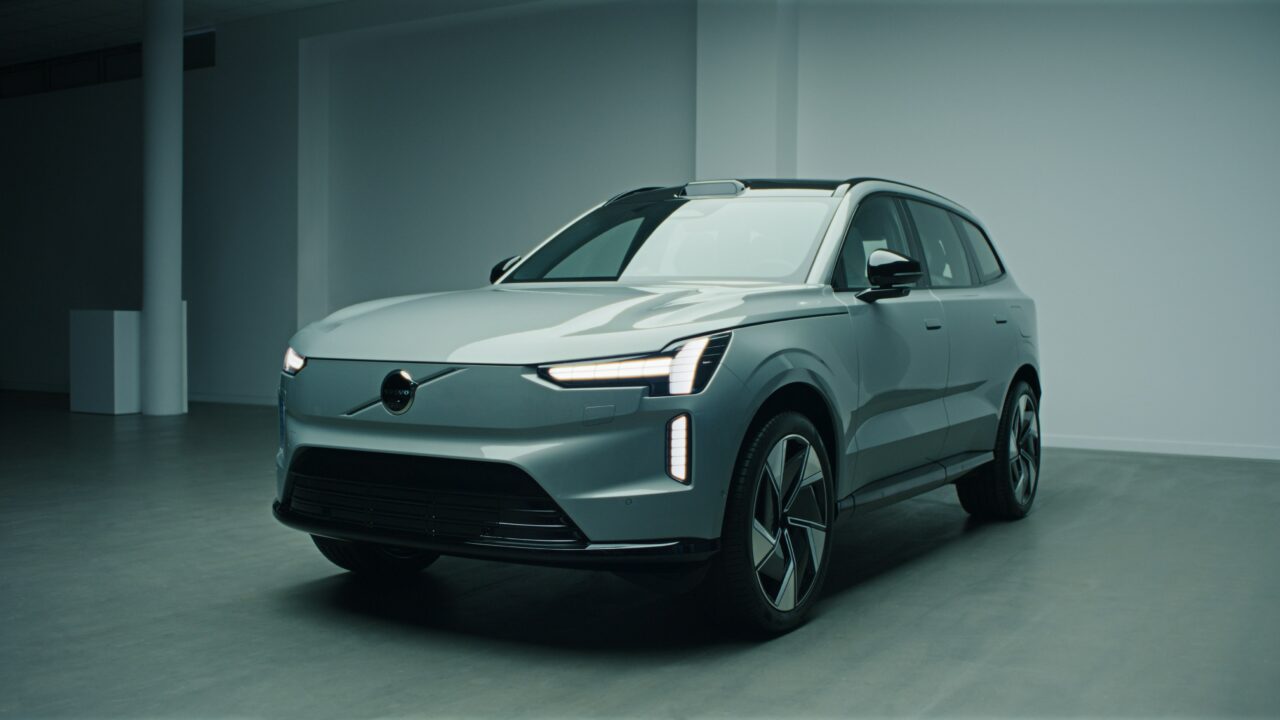
With the manufacturer planning to only offer EVs by 2030, the company estimates total battery capacity of its ‘fleet’ will reach 50GWh by the middle of the next decade.
In addition to being able to smart charge those vehicles to flexibly reduce the impact they would have on electricity consumption, the fact that the average daily journey travelled by car uses less than 10kWh and 90% of daily journeys less than 20kWh offers the opportunity to leverage the “ample spare capacity” stored in their batteries, Volvo Cars said.
The new business unit will be offering technologies and services related to energy storage and charging, starting with Volvo’s EX90 electric 7-seater SUV, a new model scheduled for launch in 2024 and the company’s first EV to be designed from scratch for electric propulsion.
Volvo’s official website page for the EX90 doesn’t list the battery sizing, although it does claim the car can do 300 miles on a single charge, while various automotive media sites and Volvo dealerships list the nameplate capacity at 111kWh.
An initial pilot project of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications is being established in Gothenburg, Sweden, Volvo Car’s home city, with the local grid operator Göteborg Energi Nät. Using an AC wallbox charger, which Volvo said will be low cost, the pilot will try out the bi-directional technology in selected local homes and the grid.
In addition to V2G applications, the company is also considering options to provide vehicle-to-home (V2H) power and vehicle-to-load (V2L) – the latter being where portable electric goods such as electric bicycles could be charged directly from the car’s batteries.
“The idea with building an energy ecosystem around your car and the batteries is that it allows you to save money and reduce your CO2 emissions, while energy firms benefit from reduced grid investments and a lower overall impact on the environment,” Volvo Cars Energy Solutions senior VP Alexander Petrofski said.
Bi-directional charging for V2G and related applications, aka ‘batteries on wheels’, have been discussed as holding great potential and being technically feasible, but carmakers have largely held back, with a couple of notable exceptions such as Nissan and its Leaf EV.
This is perhaps due to barriers such as concerns over what happens to a vehicle warranty when in dual use, and the logistics of coordinating and aggregating large fleets into grid resources.
There is also the fact that the number of EVs on the world’s roads is only now beginning to reach the kind of mass adoption levels that might offer solid business cases for the technologies, which is perhaps why we have seen increasing activity in the space in recent months.
Earlier this year, Volvo Cars invested in Canadian home energy management company dcbel to help accelerate commercialisation of the startup’s tech, including a bi-directional home EV charger designed for pairing with rooftop solar PV.
Parent company Volvo Group has also recently signed a letter of intent to jointly develop a battery energy storage system (BESS) solution using second life EV batteries with UK second life specialist Connected Energy. A separate company within the group, power solutions provider Volvo Penta, recently also entered the BESS market, offering a BESS sub-system solution.
Around the same time as Volvo’s investment in dcbel, rival BMW announced a V2G pilot in California with utility Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E). A Senator in the US state, Nancy Skinner, is currently championing Senate Bill 233 (SB 233), legislation which could make bi-directional charging capabilities a compulsory addition for EV makers.
In Europe, a trial began in June for Renault EVs to provide V2G energy with tech platform provider The Mobility House, while in August, Volkswagen’s infrastructure and utility arm Elli Group launched a digital energy trading platform aimed at enabling V2G and V2H for the parent company’s vehicles.
California Energy Commission grant funding to be announced
In related news, and going briefly back to California, the state’s energy commission is expected to soon announce awardees of grants to “accelerate the development and deployment of easy-to-use charging products which help customers manage electric vehicle (EV) charging and respond to dynamic grid signals”.
Up to US$9 million is being made available through the California Energy Commission (CEC) programme, Responsive, Easy Charging Products with Dynamic Signals (REDWDS) in the initial rollout, with a potential for a further US$300 million to be made available in a future round.
Administered under the state’s Clean Transportation Program, awardees will be required to match a minimum of a 25% share of funding, with applications closed in June.
One technology partnership, between EV charging and energy management solutions company Wallbox and bi-directional EV management software platform Bidirectional Energy said last week that it has been selected as proposed recipients for awards in the programme’s first phase. The pair will be offering an integrated bi-directional charger product from the first half of next year.
Continue reading