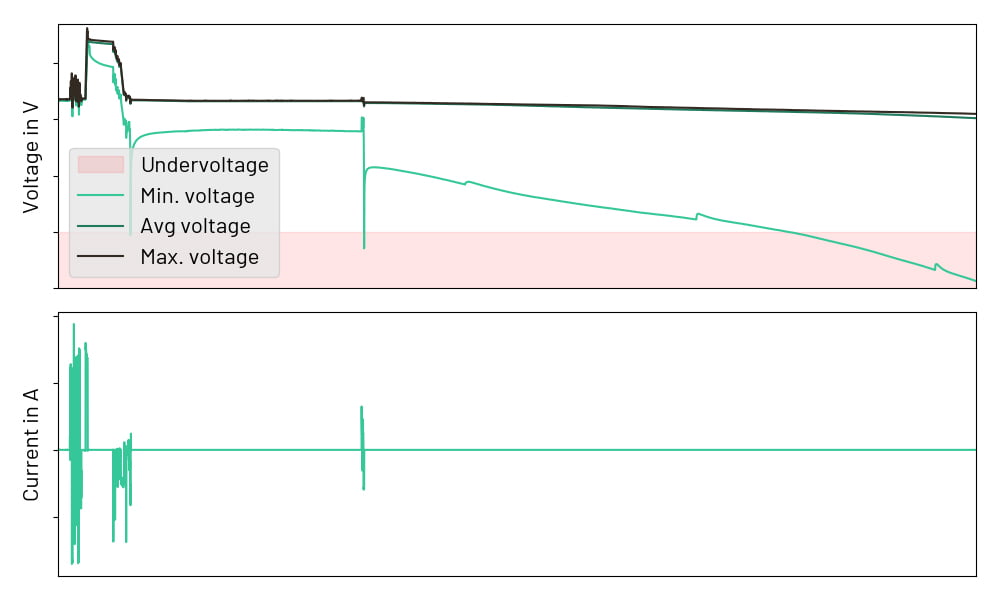
As previously reported by Energy-Storage.news, a provisional agreement between the European Parliament and Council was reached in December over the rules, which would replace a previous directive put into force in 2006. The new regulations had been first proposed in 2020, and may change again as talks progress.
Aimed at taking into account a battery’s whole lifecycle from raw materials to end-of-life and recycling, the main provisions that relate to stationary energy storage, in short, include:
Carbon footprint labelling for industrial batteries with capacity over 2kWh.
Introduction of a Battery Passport, labelling all batteries and their components with a digital pass that can be easily accessed, for example with a QR code.
Minimum levels of materials to be recovered from waste batteries: 50% recovered lithium by 2027 and 80% by 2031, an 90% by 2027 for cobalt, copper, lead and nickel rising to 95% by 2031.
Minimum levels of recycled content from manufacturing and consumer waste to be used in new batteries, to be phased in, beginning at eight years after the regulation comes into force: 16% for cobalt, 85% for lead, 6% for lithium and 6% for nickel. After 13 years, these would rise to: 26% for cobalt, 12% for lithium, 15% for nickel and 85% for lead.
Secretary general at the European Association for Storage of Energy (EASE), Patrick Clerens, said the trade association was “delighted to welcome the new Batteries Regulation as a significant step forward for the energy storage sector”.
The new Batteries Regulation is aligned with encouraging the use of energy storage to benefit the continent, whether that be behind-the-meter systems that “empower citizens and reduce energy costs for industries”, or front-of-the-meter systems that “maximise the integration of renewable energy sources and contribute to the establishment of a more resilient, sustainable, and efficient power grid,” Clerens said.
Specific points in the regulation picked out for further praise by the EASE secretary general included its focus on carbon footprint labelling, as well as the fact that it addresses end-of-life concerns, as well as how batteries can be repurposed for ‘second life’ applications.
“This legislation offers much-needed legal clarity and guidance to industry stakeholders, enabling them to effectively manage BESS at the end of their operational life,” Patrick Clerens said.
On the eve of the vote last Wednesday (14 June), trade group RECHARGE, which represents the interests of European battery manufacturers and related businesses similarly welcomed the regulation.
“Carbon intensity and due diligence provisions have the potential to not only prevent underperforming batteries from entering the EU market, but to truly work towards the climate-neutrality and sustainability objectives of the EU,” RECHARGE general manager Claude Chanson said.
“The new sustainability measures will set the rules for the game for selling batteries in Europe. This can only be successful with effective enforcement and control of the provisions. Furthermore, if correctly implemented, both the carbon footprint and due diligence have an unsurpassed steering potential to push European competitiveness based on sustainability and responsibility,” Chanson said.
Chanson highlighted too the important role the regulation could play in facilitating the EU’s decarbonisation and energy transition, but also in making the European battery value chain competitive and “able to set sustainability standards globally”.
‘Get ready for passport implementation’
Meanwhile, Energy-Storage.news also heard from the EU’s Battery Pass Consortium, put together to support the introduction of the digital Battery Passport.
In April, the consortium’s first publicly available guidance emerged, with a lengthy list of the applicable attributes of a battery that will be covered by the passport scheme and metrics for measuring and benchmarking them.
The Battery Pass Consortium’s project lead, Stepanie Schenk, told Energy-Storage.news this morning that stakeholders need to act fast to get on top of the scheme, as well as the wider regulations it is part of.
Following the parliamentary vote, which Schenk called “an important milestone” it is now in the hands of the European Council, which will formally endorse the text. It would then be published in the EU Official Journal and can then enter into force.
With an expectation the regulation could enter into force as early as August this year, the passport scheme would need to start 42 months after that, and will be mandatory for all industrial batteries over 2kWh capacity, as well as EV batteries and light transportation batteries.
“In light of this ambitious timeline, it is of utmost importance for organisations of the battery ecosystem to start preparing for the implementation as soon as possible,” Schenk said, offering up the Battery Pass Consortium “as well as other initiative in the area” that can provide guidance and a discussion forum for stakeholders.
Continue reading