More than 80,000 registrants are expected to attend Smarter E, across solar, energy storage, e-mobility and adjacent industries. That large number is not just relating to the fact that after more than three years of a global pandemic, the industry is returning to its old self, but also speaks to the rapid growth of clean energy as a business, and as a strategically important political, social and environmental concern.
We kick off our blog today with a quick look at some insights from industry experts, on the topics framing the conversation.
DNV survey: Solar-plus-storage is crucial to energy transition
“Global emissions are continuing to rise; the good news is that we have the technologies to prevent further increase of emissions. Combining solar and storage also opens a wide range of possibilities to provide 100% renewable energy for society in a reliable and cost-efficient way.”
Those are the words of Ditlev Engel, CEO of energy systems at DNV. According to a survey of industry professionals conducted recently by the standards and certification group, 92% said that solar-plus-storage is a powerful tool to increase efficiency and resiliency of global energy networks.
Called ‘Trilemma and Transition,’ the 50-page survey covers a wide range of topics, with views of more than 1,300 senior industry workers canvassed from energy generation and solutions providers to large end-users.
The trilemma referred to, by the way, is the need to increase energy sustainability, affordability and security, all at the same time. DNV found that while policy and regulatory changes are needed all over the world to better tackle this convergence of priorities, businesses are for their part developing new business models and working together.
“It’s important that we act fast for the collective good, remove barriers for clean energy and plan for long term progress,” Engel said.
The DNV Industry Insights survey is conducted alongside the publication of the group’s Energy Transition Outlook series.
Making energy industry forecasts out to the mid-21st Century, DNV is predicting that not only will solar PV markets grow 20 times over by 2050, but that solar uptake increasingly goes hand-in-hand with energy storage over that time.
For example, within 10 years, about 20% of all new solar will be coupled with energy storage, and by 2050, that figure will be closer to 50%.
One really interesting insight is that while adding energy storage does of course increase the cost of investing in solar PV, the added value of storage in solar capture price is already tangible. Being able to store energy generated during daylight hours for sale when demand rises will by 2038 mean that “capture price advantage” will outweigh the cost of the storage system.
With solar PV plants expected to last about 25 years in operation and battery storage systems roughly 10-15 years, planning for that scenario already needs to be ongoing.
More than two-thirds of solar industry professionals surveyed said they already have revenue-generating business interests in the storage sector, and more than half expect to increase their storage investments within the next year.
However, worker and skills shortages, and uncertainty over public policy direction remain the biggest threats perceived to the rapid uptake of solar and storage, while permitting and licensing processes were cited by 87% of solar industry respondents as critical to achieving net zero targets.
Apricum: Clean energy finance expert’s take on top trends
The EU’s recognition of the importance of energy storage, standardisation of system integrator offerings, progress in lithium and alternative battery technologies and the growth of artificial intelligence (AI) are among topics set to frame conversations at ees Europe, according to Florian Mayr, partner at Apricum – The Cleantech Advisory.
The clean energy finance expert highlighted six trends to look out for at the show in a recent blog post on Apricum’s website.
In short, these are:
System integrators continue to play a core role, and their strategies and technology choices both follow and set directions the industry takes. Mayr noted that two key trends shaping that direction today include a greater degree of system standardisation from major players like Fluence, Tesla and Wartsila, and an increase in the “comprehensiveness” of their offerings. The big players’ battery energy storage system (BESS) solutions are increasingly delivered to customers as modular, easily replicable factory-produced products, rather than heavily customised project-to-project systems seen in the past. At the same time, system integrators are more frequently offering turnkey BESS solutions, incorporating hardware and software from power conversion systems (PCS) to transformers, while many now also include EPC and O&M services in their suite.
With the recent European Union (EU) Electricity Market Reforms, currently in their draft stage, the union has included energy storage as a key flexibility resource. Its proposals include removing or lowering grid fees for storage, making storage eligible for capacity markets, and the need for regular assessments of the pace and scale of storage adoption in Member States. Alongside that, there is also the Net-Zero Industry Act, described as comparable to the US’ Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in promoting the manufacturing value chain for clean energy, including energy storage.
An increasing interest in alternative technologies has been observed, Florian Mayr wrote, partly because of lithium-ion supply chain challenges, but also because of new tech that could deliver on applications such as long-duration energy storage (LDES) that lithium traditionally has not been considered for. Sodium-ion could be an immediate competitor or successor to lithium if it can find scale and the technology meets market demands, but other battery tech, from sodium-sulfur and flow batteries to zinc, plus thermal and mechanical storage technologies, could all find a place – if cost reductions can make them competitive.
AI-powered software is quickly enabling asset owners to increase renewable energy penetration, improve efficiency, reduce cost and maximise revenues from market participation, according to Florian Mayr. For energy storage, the two key areas where this is being achieved are in optimising the dispatch of assets, and in providing predictive maintenance.
The commercial and industrial (C&I) segment of the market is largely “dormant”, Mayr wrote, and this is being played out not just in Europe but in other markets like the US too. Low energy prices and relatively high storage system costs have for a long time rendered most C&I use cases economically unviable, but the events of the last year or so, resulting in “sky-high” electricity prices is changing the dynamic, according to Florian Mayr. Corporates are also seeing energy storage as a key enabler for onsite renewable energy consumption.
According to the Apricum partner, the past 18 months have been “exciting” for developers of large-scale storage, due to an “abundance of equity for financing grid-scale storage,” from an increasingly diverse set of backers. That said, Europe’s biggest and fastest-growing energy storage market to this date, the UK, is seeing a saturation of key markets for ancillary services and Florian Mayr said this is precipitating a shift towards financiers moving into continental markets in Europe. Mayr pinpointed four countries as emerging leaders: Italy, Belgium, Germany and Poland, but with the ongoing European policy, regulatory and fiscal shifts to support clean energy, it seems likely the whole of Europe will see an uplift in activity. However, Apricum has concerns that only a small number of lenders are making credit available for storage, that lending structures are often fairly localised and may not support European uptake uniformly across the continent and that while developers and transmission system operators (TSOs) favour larger projects, this is not always the case with lenders.
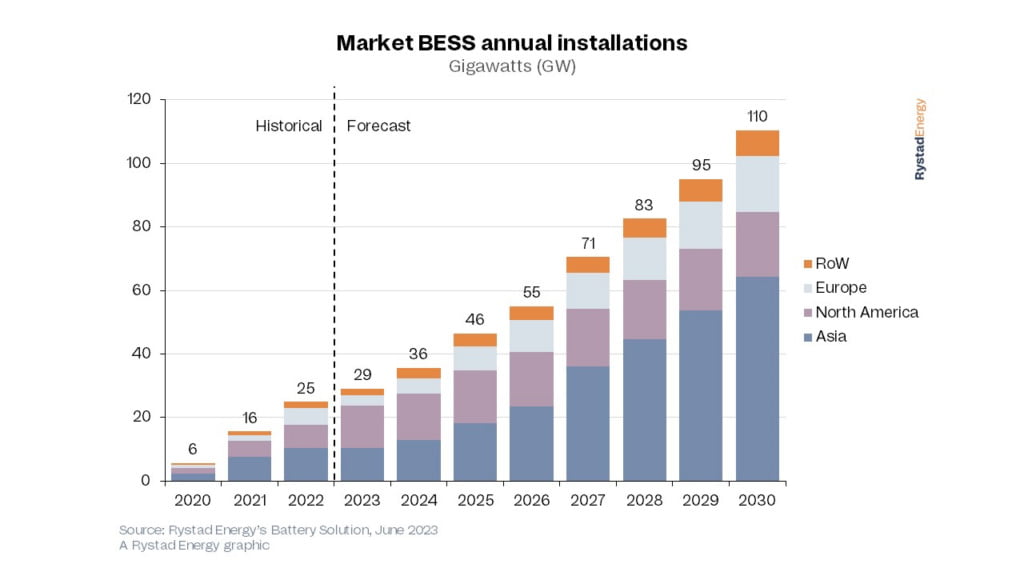
Data & images: Rystad Energy’s Battery Solution analysis service.
Rystad: 18GW annual market in Europe by 2030
Energy industry analysis group Rystad Energy has forecast that by 2030, annual BESS installations worldwide, across all scales, will total 110GW and 400GWh.
Of that megawatt figure, Europe will be the third biggest market, after Asia and North America, with Rystad Energy forecasting 18GW of annual installations on the continent.
The European market for residential storage looks particularly strong, due to incentives and high grid electricity prices, while the European Green Deal Industrial Plan will support BESS developers as the policy package seeks to support the European economy’s transition to sustainable and low-carbon industry.
Continue reading