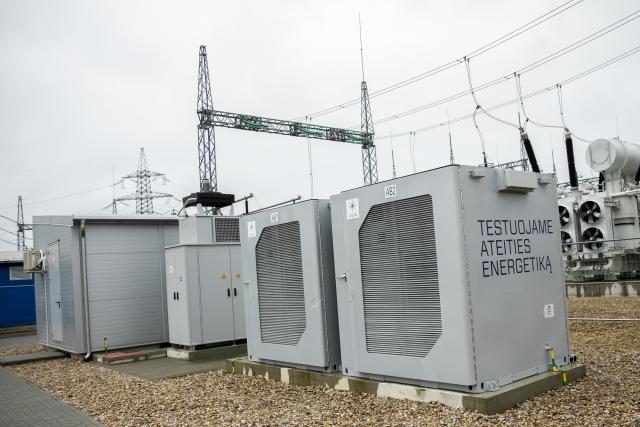
The company has opened up the procurement of its first 25MW/50MWh BESS to competitive solicitations in a tender that will be open internationally. The aim is to determine that the technology is suitable for scaled deployment in Estonia, as well as in the other markets Eesti Energia serves.
The BESS will be installed in Ida-Viru, Estonia’s most north-eastern county, which contains rich shale oil deposits, which is the main mineral mined in the country, with shale oil-to-electricity representing a major part of Eesti Energia’s business today.
However, the utility is targeting exiting electricity production from shale by 2030, and then by 2040 to have retooled its shale business to instead produce raw materials for the chemical industry, having ceased production of liquid fuels from shale oil by that time.
The company also needs to meet expectations and needs of the Estonian state, which include raising the share of electricity generated from renewable energy to at least 40% by 2030 while ensuring stable revenues and stable supply of electricity.
Energy storage will be a key tool in facilitating the rapid uptake of renewable energy, Eesti Energia board member Kristjan Kuhi said, adding that a system based on renewables would not have been subject to the same intense spikes in the prices of electricity felt across Europe after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Storage systems can be used to mitigate high peak pricing while enabling the storage and dispatch of renewable energy, Kuhi, Eesti Energia’s development manager for energy solutions said.
Towards the beginning of this year, regulators in Estonia gave approval for its first-ever pumped hydro energy storage (PHES) plant, due to begin construction in summer 2024 following the conclusion of a tender process, which is anticipated by the end of 2023.
The 550MW/6GWh PHES plant, in development by Estonia-based holding company Alexela and two co-owners of the project, will play into the Nord Pool Spot power market.
Lithuania, Ukraine also recent adopters of BESS technology
It will be interesting to see how closely Estonia’s energy storage development path mirrors that of another Baltic state, Lithuania. Global energy storage system integrator and services provider Fluence is currently thought to be putting the finishing touches on a four-project, 200MW/200MWh portfolio of BESS installations for Lithuanian state-owned energy group EPSO-G and its special purpose company formed for the project, Energy Cells.
Part of the motivation for the Lithuanian project on transmission operator Litgrid’s networks is to further the country’s energy independence from Russia and facilitate synchronisation with other European power networks. It follows an initial 1MW pilot project (pictured above), on which installation was completed in 2021.
Ukraine’s first grid-scale BESS pilot was completed just a few months before the invasion, again playing a key part in de-coupling the country’s energy networks from dependence on Russia – and effort that is ongoing and has been expedited, despite the impact of the brutal war. Towards the end of last year, the World Bank said it would finance a tender for further BESS projects in Ukraine, to be built at existing run-of-river and pumped hydro energy storage (PHES) plants
Eesti Energia did not discuss its forthcoming pilot project in the context of those geopolitical concerns, focusing instead on the energy transition and potential economic benefits of BESS technology in its release yesterday.
The company did however announce its own planned 225MW PHES plant last year, stating then that it would aid a wider push for independence from Russia, proposing the plant to also be located in Ida-Viru at the site of a disused shale mine.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher, Solar Media, will be hosting the 1st annual Energy Storage Summit Central and Eastern Europe this year, 26-27 September 2023 in Warsaw, Poland. See the website for more details.
Continue reading