Then, just a day or two later, it was revealed that financial close has been achieved on Oneida Energy Storage Project, a flagship project supported at various stages by both Ontario’s provincial government and Canada’s federal government.
At 250MW, the scale of Oneida is significant in megawatt terms as a step into the sort of scale we’re more commonly used to seeing south of the border in the US than in Canada. What’s perhaps even more interesting is that at 1,000MWh, the project is a rare early example in the country of a 4-hour duration large-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) project.
Flagship project helps lay groundwork
The contracts awarded in Canada’s largest-ever energy storage procurement are only the first tranche being made by the IESO, regular readers of Energy-Storage.news will know. Back in October last year, the Ontario government said it would be making a procurement of a total 4,000MW of energy resources.
That would include between 1,500MW and 2,500MW of storage, together with natural gas, the latter representing expansions or extensions to contracts for existing thermal power plant facilities rather than new-build.
The primary function of those resources will be in contributing to resource adequacy (RA), Patrick Bateman, an independent consultant currently working with the national trade association, Energy Storage Canada, says.
The most populous province in Canada isn’t struggling to meet its electricity demand today, but is projected to be challenged as demand growth is projected into the middle of this decade.
Nuclear retirements and refurbishments will be taking some of that capacity offline, while Ontario is experiencing load growth, from a combination of electrification of transport, buildings and industry. The latter includes a proliferation of steel and aluminium plants that will be adding “some very, very significant amounts of load to the grid”.
In addition to providing that “firm, dispatchable capacity,” Bateman says, the contracted resources will be allowed to play into merchant market opportunities, which could include ancillary services.
The IESO made its electricity demand forecast back in 2021, recommending that new resources be procured and online by 2027 as the situation begins to get tighter from 2025, leading to the tender, LT-1, being conducted on an expedited timeline.
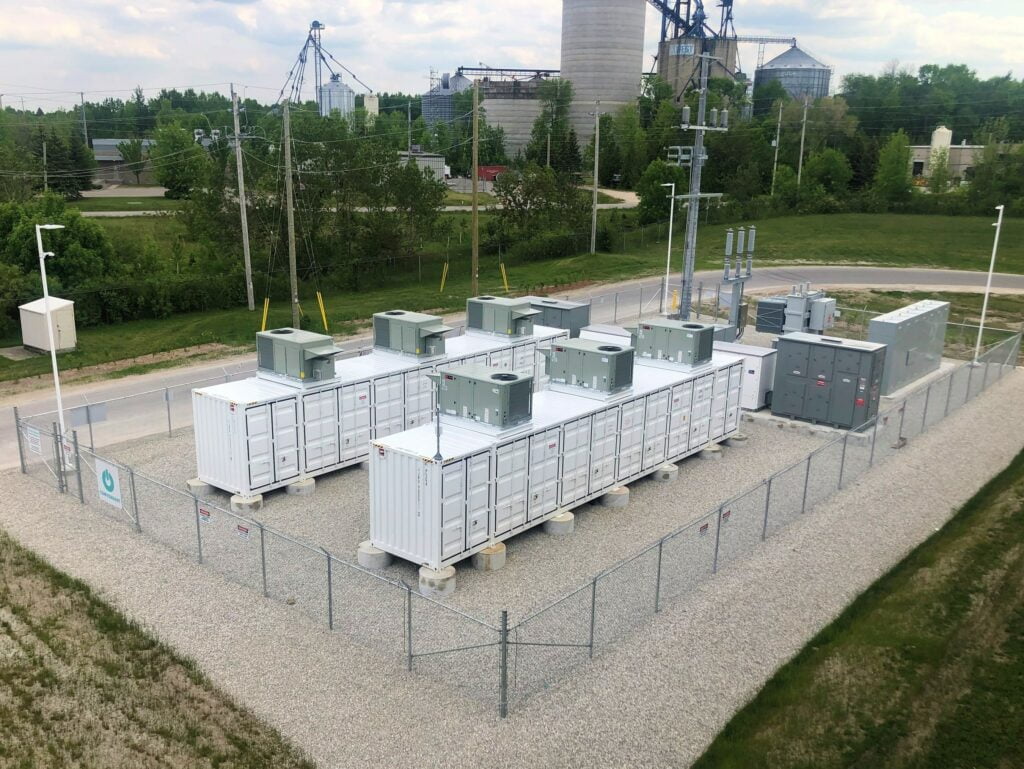
Ontario’s biggest BESS projects to date have been large-scale behind-the-meter resources for industrial facilities to reduce their Global Adjustment demand charges, like this one. Image: PRNewsfoto/Convergent Energy + Power)
Resource adequacy rewards longer-duration resources
A term we most frequently associate with California, resource adequacy is, as the name suggests, ensuring sufficient energy is available to cover demand. It’s what has driven California to become an early adopter of 4-hour duration battery storage, in the same way it was an early adopter of solar PV and shorter duration lithium-ion BESS at scale.
What that means for sunny California is that the state tends to have abundant solar resources during the daytime, and clearly less so in the evening.
While batteries aren’t yet commonly used to cover all of those evening and nighttime hours, being able to use four hours of storage between the evening peak hours from 5pm to 9pm each night has significant benefit in reducing the need to rapidly ramp up, control and dispatch thermal resources as soon as the sun starts to go down.
While Ontario’s situation isn’t precisely analogous to California’s, it’s telling that at least some of the publicly revealed winners of the LT-1 procurement have done so with bids for 4-hour duration BESS.
Developer Boralex was the biggest winner in the tender, awarded contracts for 380MW nameplate power output from two projects, both of which are 4-hour duration. Furthermore, at 300MW/1,200MWh, Boralex’s Hagersville Battery Energy Storage Park will be even bigger than the Oneida project.
Step-change in scale of procurements
So, Oneida, which has an expected capital cost of about CA$800 million (US$587.15 million) to get commissioned, will be the biggest project in Ontario and in Canada for perhaps only a short time from 2025, when it comes online, until Hagersville does. And perhaps other even bigger projects might come up from the next round of LT-1 – we wouldn’t bet against it.
But, even when Oneida is overtaken as the biggest BESS in the province, its status as a historic project for Canada’s energy storage sector seems assured.
Jason Rioux, chief development officer at NRSTor, the Canadian energy storage pioneer which has formed a joint venture (JV) with the Six Nations of the Grand River indigenous community to co-develop the project, says work done to get Oneida off the ground can benefit the industry, the IESO and perhaps the whole country in the long run.
Having done “many deals” with the IESO in the past for smaller projects using varying technologies, NRSTor went through a couple of years of negotiation with the system operator during the five years or so Oneida’s development journey so far has represented. It has even directly contributed to the IESO’s ability to host the LT-1 procurement, Rioux says.
“We’ve gone through a special gating process established to digest this project and see it move forward, and the nature of a couple years of contract negotiation with the IESO gave, I think, a lot of the foundation for understanding how to bring on large scale energy storage in the province of Ontario.
“…it has really helped the IESO scale up to a larger procurement process that is based on some experience, bringing a project to fruition and financing a large-scale storage project in this market.”
Indeed, for the IESO, it marks a big step-up. It first procured energy storage in 2012, awarding just 6MW of regulation services contracts to two projects, while subsequent procurements in 2014 and 2015 awarded 28.8MW and 11.75MW respectively.
Merchant risk and contracted revenues combine
Perhaps one area where that series of discussions over Oneida helped most was in shaping a long-term contracting structure for storage that would also give developers the ability to also earn revenues from other applications on top of providing resource adequacy.
Oneida has a 20-year agreement in place, giving the IESO rights to charge and dispatch the BESS to meet its peak load, called an Energy Storage Facility Agreement (ESFA).
Northland Power, also in the consortium developing Oneida, said last week that it expects about 60% of the revenues it earns from its 72% stake in the project will come from the ESFA, and the rest will come from the wholesale market, including ancillary services opportunities.
Jason Rioux of NRStor says the Oneida journey, as he called it, has been characterised by the “trials and tribulations with launching a larger-scale project and getting it financed in a market that has some contracted revenues, and some merchant revenue exposures all mixed up together”.
The balance that needed to be struck, he says, was to do that “in a way that puts appropriate risk on developers and owners of the projects and delivers the best value possible to the ratepayers in Ontario, electricity consumers in Ontario”.
And that, at the heart of it, may well resonate with folks working in other markets around the world. A similar approach is being taken by authorities and electricity network operators in New York and in Australia. Germany’s Innovation Tenders for hybrid clean energy projects, which have already been launched, are also not dissimilar.
Tenders are set to be launched in both of those regions where contracts awarded are expected to be long-term agreements that offer stable returns for developers and investors, giving them that much-craved revenue certainty. At the same time, they will be able to – and perhaps need to – take a degree of merchant risk to make profits.
Developments in Ontario and Alberta, Canada’s leading provinces for energy storage by pipeline and installed capacity, are in focus in the upcoming Q2 2023 edition of our quarterly journal, PV Tech Power (Vol.35). Digital subscription to PV Tech Power is included in your Energy-Storage.news Premium access.
Continue reading