The projects will help stabilise the electricity grid, reduce interventions and reduce system costs. The Grid Booster initiative was launched three-and-a-half years ago in Germany and could see the country’s TSOs, of which there are four major ones, deploy as much as 1,300MW to help replace the function of additional transmission infrastructure, and do it more cost-effectively.
“We are pleased to have received confirmation from the BNetzA for this innovative technology. The decentralized grid booster will help Amprion and E.ON to keep the electricity grid stable and at the same time reduce the costs for grid interventions and thus the grid fees in Germany,” says Amprion CEO Hans-Jürgen Brick.
Amprion claimed it would be the world’s first decentralised Grid Booster, with the first to be deployed in the area of LEW Verteilnetz (LVN), a regional network operator of E.ON, in Bavarian Swabia. That first project is expected to come online in 2026.
The projects will help to counteract grid overloads when faults occur in the transmission network to ensure consequential damage is prevented. Battery storage technology’s near-instantaneous reaction time also means the system operators do not need to reduce equipment utilisation through preventive re-dispatch before the fault occurs.
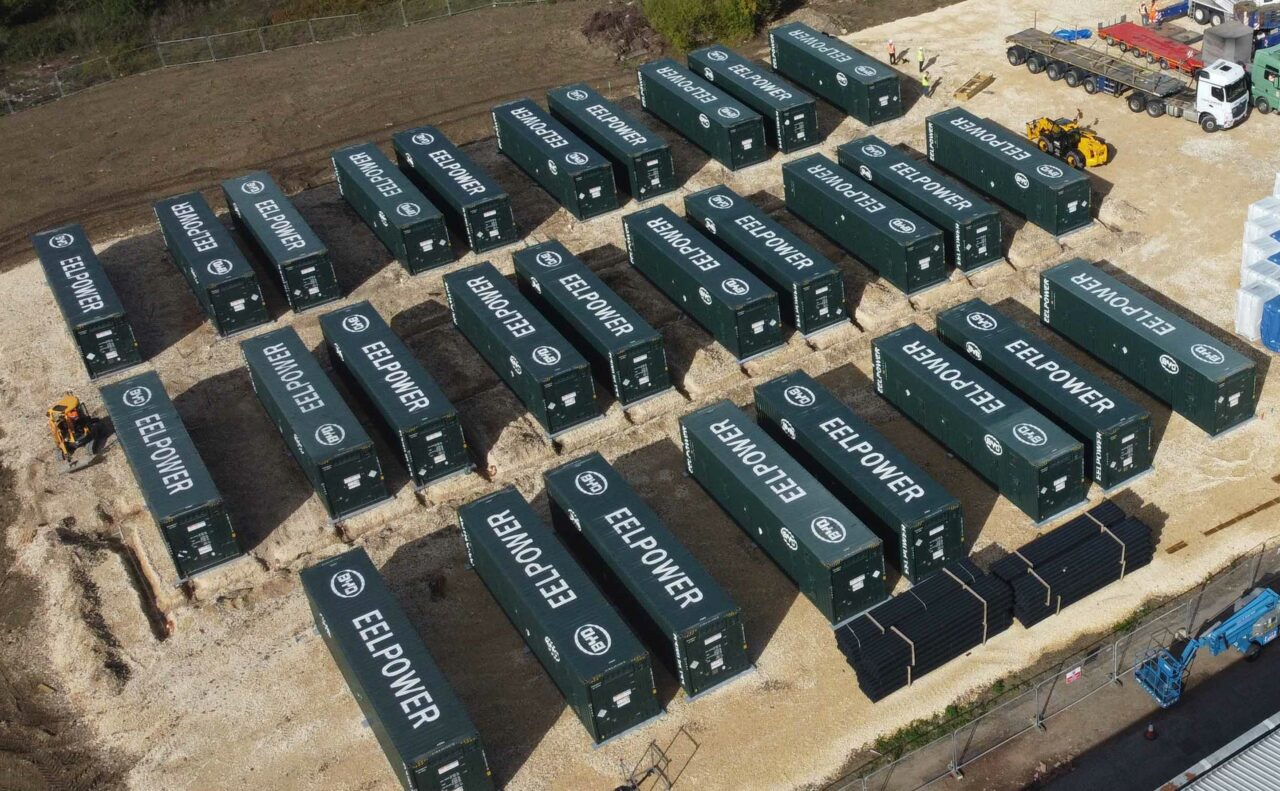
The companies said the project will be the first time the Grid Booster concept has been done using several smaller battery storage projects at the distribution level. It did not reveal the technology provider that would deploy the battery storage systems.
“This structure reduces connection costs, increases the availability of the entire storage system and improves flexibility in the distribution network. The modular components can also be implemented faster and have less impact on the environment. The grid booster also reduces the need for interventions in the grid,” Amprion’s announcement read.
The TSO is the third in Germany to make a firm announcement of its portion of the Grid Booster projects.
TenneT has announced plans to deploy two 100MW systems for 2025 while TransnetBW last year enlisted global battery storage system integrator and operator Fluence to deploy a 250MW project, also for 2025. Energy-Storage.news is not aware of firm announcements being made yet by 50Hertz Transmission, the fourth.
Fluence has made the non-wires alternative Grid Booster transmission sector a priority target segment for its future energy storage projects. It recently revealed it has secured a third order within the space, following on from the Germany project with TransnetBW and one in Lithuania.
Amprion is responsible for the transmission network in the western part of Germany.
Continue reading