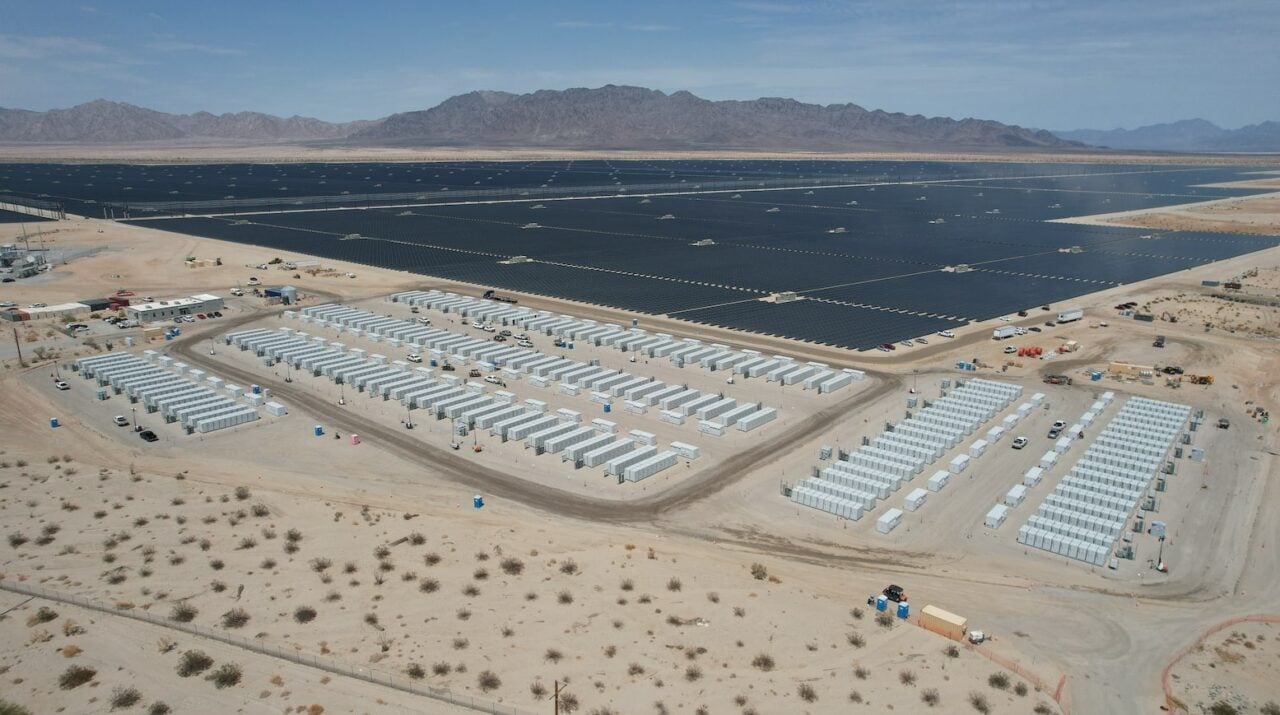
CPA is one of 25 community electricity providers set-up as part of California’s Community Choice Aggregation (CCA) scheme providing electricity as an alternative to investor-owned utilities. The organisation is the biggest among the state’s CCAs, with electricity supplied to around 3 million customers in 35 Southern California communities in Los Angeles and Ventura counties.
The organisation representing the interest of California‘s community choice electricity providers, known as California Community Choice Association (CalCCA), said in a statement released last week that the PPAs were the 45th and 46th long-term energy agreement signed by CPA. The recent contracts increase CPA’s energy storage capacity within its overall energy portfolio to 1,934MW.
A few days after the meeting, Clean Power Alliance announced its annual request for offers for energy resources including standalone energy storage, renewable energy generation, renewables-plus-storage hybrids, resource adequacy (RA) and dispatchable thermal energy with RA contracts.
Energy storage resources entering the RFO, which is hosted on the Ascend Analytics Energy Exchange (AEX), must be a minimum of 15MW and 10-year and 20-year contracts are being offered for qualifying storage and hybrid storage projects.
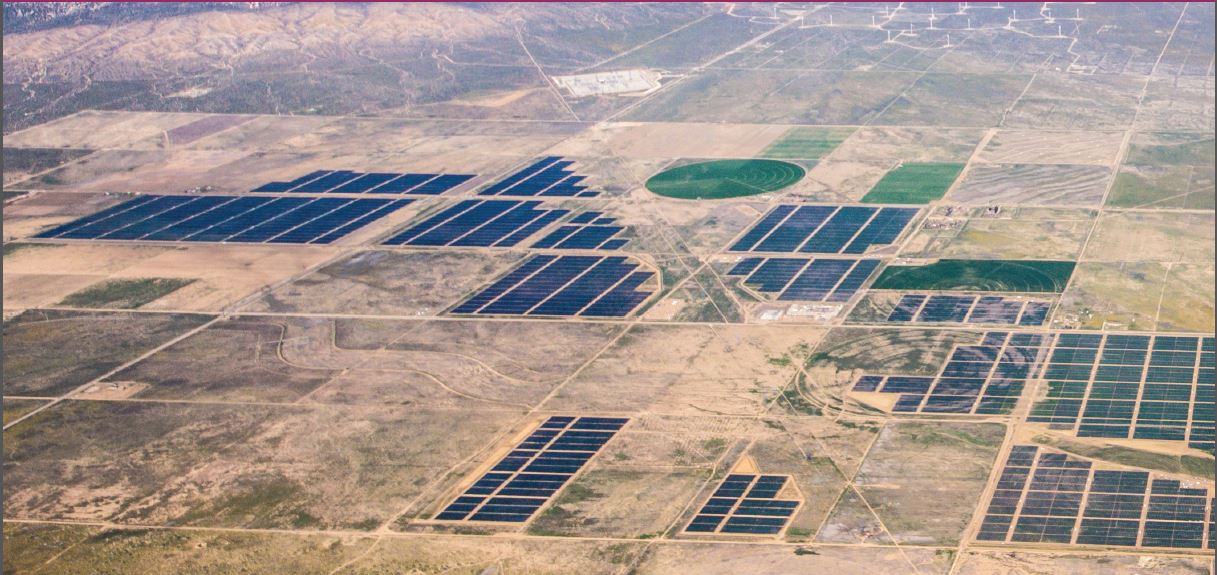
Solar Star complex
Under the terms of the agreements, CPA will receive energy from two identically sized solar and battery storage facilities being developed by BHER at its Solar Star complex located approximately 7 miles southwest of Willow Springs in Kern County, California. The Solar Star Solar 3 + 4 facilities will each comprise a 24MW photovoltaic solar facility co-located with a 23MW/92MWh lithium-ion based BESS.
The Solar Star 3 and 4 facilities will interconnect to the CAISO-controlled grid via Southern California Edison’s (SCE’s) Whirlwind 230kV Substation. The two new developments will be located nearby BHER’s operational Solar Star 1 and 2 facilities which have 314MW and 265MW of solar capacity, respectively. BHER sells the energy generated by the two solar-only projects to SCE under separate long-term PPAs.
BHER has secured CAISO interconnection agreements for the two new Solar Star developments (queue no’s 1323 and 1324), along with necessary land use permits and approvals under the California Environmental Equality Act (CEQA). The Solar Star 3 facility is expected to be brought online in July 2025 and the Solar Star 4 project is anticipated to come online a month later in August 2025.
CPA will pay BHER a fixed price per MWh for energy and a kW-month fee for the energy storage capacity. The agreements include energy, ancillary services and resource adequacy.
Tight supply market
The PPAs relating to BHER’s Solar Star 3 + 4 facilities were selected by CPA after the developer submitted an offer outside of the electricity provider’s annual RFO procurement process.
In September 2023, CPA commenced negotiations with the developers of 10 projects which it had selected as part of its annual RFO procurement and put another 17 projects on a waiting list. In the agenda packet for the June 7 meeting, CPA stated that although it had secured four agreements as part of last year’s RFO, none of the remaining shortlisted or waitlisted projects remained viable.
CPA blamed the lack of available projects on a tight supply market caused by numerous factors including “delays to project interconnections, scarcity of projects with Full Capacity Deliverability Status (FCDS) and rising financing costs.”
CPA said it will continue to explore capacity procurement through bilateral offers in addition to its annual RFO process which seeks to fill a large portion of its energy portfolio with long-term contracts and reduce the need to purchase energy in volatile short-term markets.
Warren Buffet-owned Berkshire Hathaway
BHER is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway Energy Corporation – a holding company owned by investor Warren Buffet’s multinational conglomerate Berkshire Hathaway, Inc.
Berkshire Hathaway also owns utility NV Energy which recently announced a PPA with developer Arevia Power covering 700MWac of solar capacity and 700MW/2,800MWh of energy storage capacity from the developer’s Libra Solar project located in Mineral County, Nevada, as reported by Energy-Storage.News earlier this week.
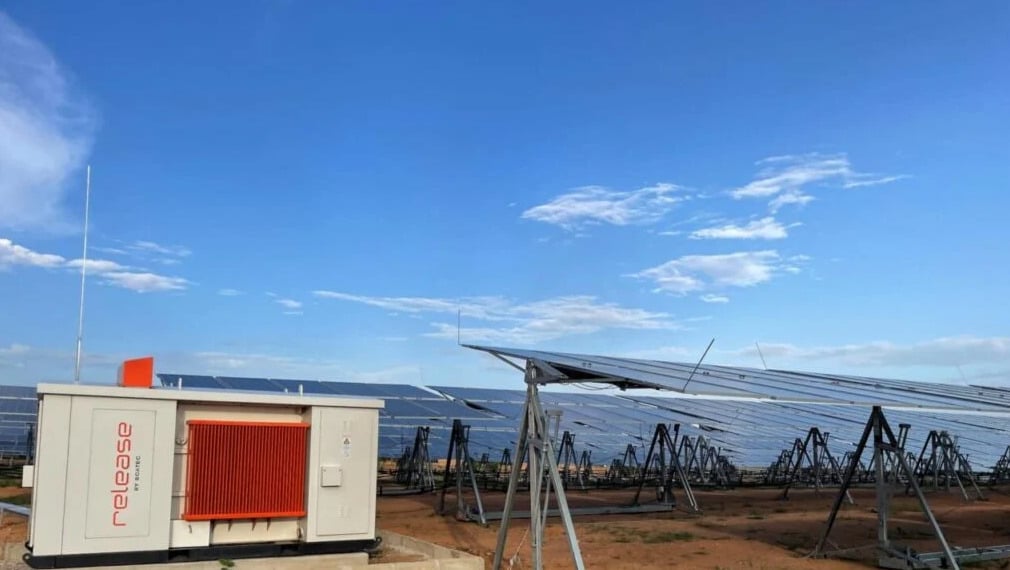
Scatec doubling solar and storage projects’ capacity in Cameroon
The expansion will increase the size of Release’s Cameroonian portfolio to 64.6MW of solar capacity, alongside 38.2MWh of batteries, and follows a US$26 million investment made into the projects.
“This extension is a testimony to the success of the initial projects and to the benefits provided by our innovative offering,” said Release CEO Hans Olav Kvalvaag. “By increasing the installed capacity in the country, we are reaffirming our collaboration with ENEO and our commitment to Cameroon as a key market for our solutions.”
The two projects were initially developed alongside African engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) firms Izuba Energy and Sphinx Energy. The next round of expansion work will be partially funded by Climate Fund Managers, a Dutch investment group, which reached an agreement to provide Release with US$102 million in financing last July, in exchange for a 32% ownership stake.
See the original version of this article on PV Tech.
Energy storage to reduce market risks for CfD projects as Ørsted takes FID on Hornsea 3 BESS
The BESS, which will use Tesla Megapacks, and wind farm are set to enter commercial operation in 2026/2027. It will help reduce price volatility, provide services to the market operator National Grid ESO and help the buildout of renewable generation.
Hornsea 3 won a contract under the Contracts for Difference (CfD) scheme in July 2022, a programme in the UK which provides renewable generation projects with guaranteed revenues via a strike price and cap-and-floor mechanism that provides a top-up payment if revenues fall below a certain level.
The roughly 10:1 wind-BESS sizing opted for by Ørsted is in line with other wind co-located BESS in the UK market.
Energy storage reducing market risk for CfD projects
CfDs nonetheless still leave projects open to market risks and the UK’s growing BESS fleet is helping to mitigate these, as consultancy AFRY’s senior principal John Perkins explained to Energy-Storage.news.
“Where I see storage becoming relevant for CfD projects is on negative prices, which storage can help reduce,” Perkins said.
Ørsted is co-locating its BESS with Hornsea 3, building it on the same site as the onshore converter station. Energy storage’s role in integrating intermittent renewable generation onto the grid is well-known but for CfDs, a specific and significant benefit is reducing the amount of negative pricing, where generation is so high that prices go below 0.
“For recent CfDs, if the price goes negative for six hours consecutively you lose the top-up payment. Future CfDs will have this applied for even one hour. That was introduced because without it the CfD risked a problematic market distortion, with no incentive to curtail.”
“Negative prices are about 100 hours of the year right now, it’s become a problem and a big risk for generators. And there is short-term potential for negative prices to grow, perhaps to several hundreds of hours though maybe not to 1,000 a year.”
Energy storage can also help reduce market risks for CfD projects around imbalance costs, as Perkins explained: “CfD wind receives fixed income per megawatt hour, but it is exposed to market risk on its imbalance costs. Greater storage deployment, and therefore a smoothing of imbalance prices, is a benefit to CfD generators. It helps reduce the costs associated with its forecast error and balancing.”
Essentially, balancing costs for managing forecasting errors would go up and up without energy storage, but storage can keep those costs at lower levels, further reducing market risk.
Offshore wind has been the primary beneficiary of CfD allocations although in the last procurement. During Auction Round 5 (AR5), in September last year, no offshore wind was granted funding, as reported by our sister site Current. However, some are optimistic that the next round, AR6, will see more successful wind projects win contracts.
Tackling transmission system constraints
Curtailment of renewable generation can also happen due to transmission system constraints, particularly a problem for energy being transported across the Scotland-England border. Storage can help there too, Perkins said.
“Right now the balancing mechanism (BM) can protect generators with CfDs by allowing them to recover the balance of their CfD. But, some CfD projects are now getting non-firm agreements which means you won’t be protected in the same way. And storage has potential to help there as well, by helping National Grid with some of the system reasons that would drive more curtailment, essentially by acting as a transmission asset.”
To this end, transmission system operator (TSO) National Grid recently launched a constraint management intertrip service (CMIS) market. Zenobe, one of the UK’s largest BESS developer-operators, has a BESS project in the first one and while another developer-operator, Field, is proposing a significant expansion of that market, Perkins added.
Ørsted, mainly known for wind, is also active in renewables and storage in the US and is considering deploying a large-scale project using the novel ‘CO2 Battery’ long-duration energy storage (LDES) tech from Energy Dome.
Europe’s battery storage deployments doubled in 2023, policymakers must support continued growth, says SolarPower Europe
Alongside the report’s launch, SolarPower Europe has called for the European Union (EU) to adopt a comprehensive energy storage strategy and a 200GW by 2030 deployment target which it said would fully unlock solar PV growth potential in the bloc.
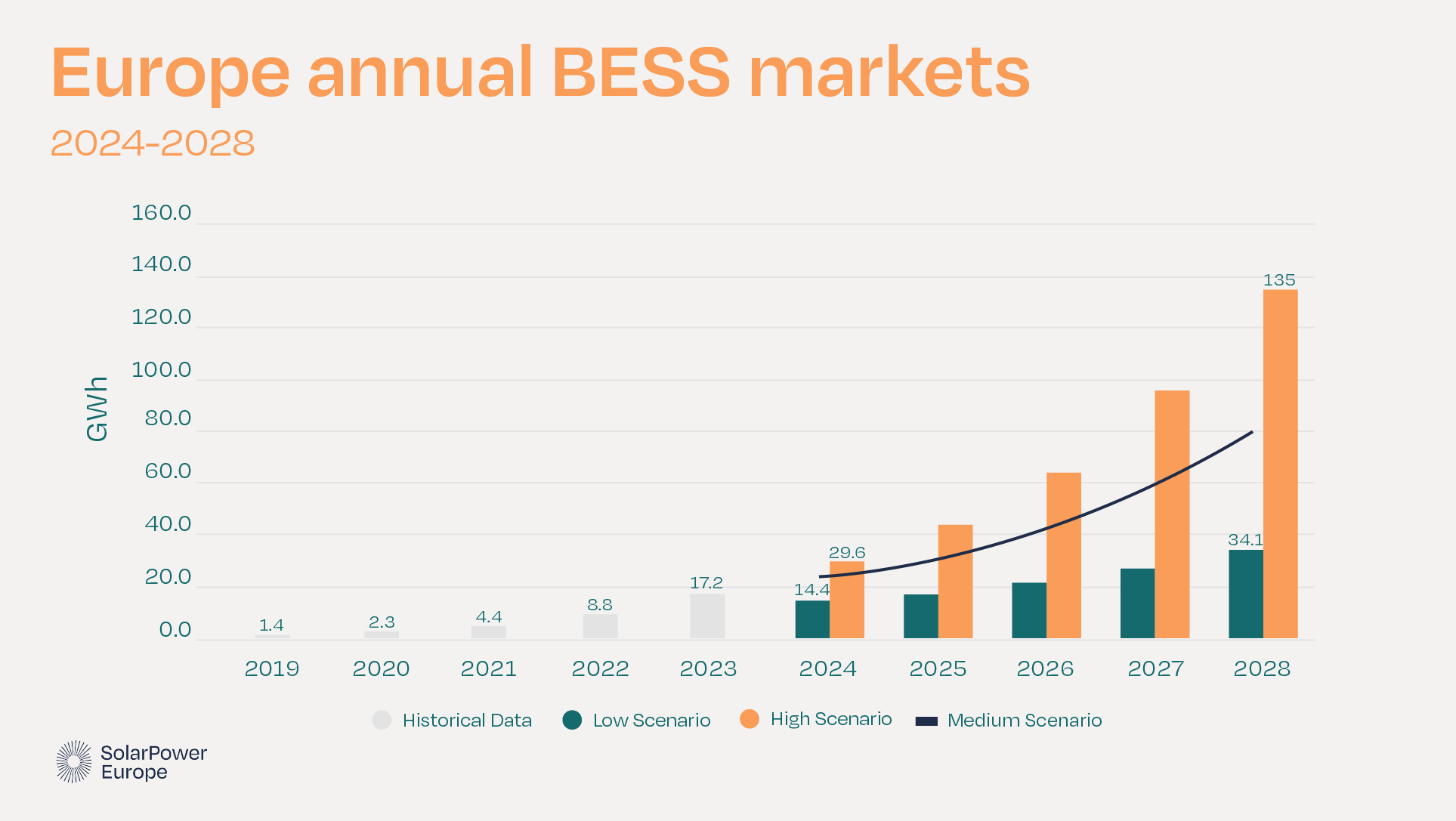
The association’s analysis found that 17.2GWh of battery energy storage system (BESS) installations were made in 2023, a 94% year-on-year increase from 2022, after a similar percentage increase the previous year. Looking back at a decade of data, it is a far cry from 2014 when Europe-wide deployments totalled just 150MWh for the year.
In fact, the market has doubled or close to doubled in size now for three consecutive years, and the total fleet across Europe represented 35.9GWh of energy storage capacity by the end of 2023.
Nonetheless, this lagged behind the global pace of deployment, with Europe accounting for just 15% of all worldwide additions, which grew by 133% last year by contrast.
SolarPower Europe said that with around 40% of energy consumption across the continent being met by renewable energy sources, battery storage is increasingly becoming the most crucial tool for integrating renewables on the grid.
However, realistic assessments of the need across Europe are lacking, as are supportive policies and market environments that would enable the deployment of around 200GW of battery storage, which SolarPower Europe estimated would be needed by 2030 in the European Union (EU) Member States alone to meet their agreed renewable energy goals.
The rapid growth seen in the past three years has been driven largely by private individuals as the Russia-Ukraine war sparked an energy price crisis and fears over security of supply, combined with falling costs of battery storage technologies over the past decade.
SolarPower Europe predicted a slowdown in growth over the next three years, forecasting growth rates in the range of 30% to 40% annually between 2025 and 2028, and it is now the turn of policymakers to support energy storage and its role in the energy transition, the trade group said.
“Growing battery storage and flexibility represents a fundamental shift from our current grid-centric view of the market. It impacts not only the way we plan infrastructure and the way we operate the system, but also the markets we engage with,” SolarPower Europe CEO Walburga Hemetsburger said, adding that EU Electricity Market Design (EMD) reforms which would set Member States targets for adding flexibility to their grids must be implemented as soon as possible.
“The new Electricity Market Design (EMD) legislation lays the groundwork for a more robust energy policy,” Hemetsburger said.
“We need to urgently implement these measures and call on the European Commission to report on the EMD implementation ahead of the first Energy Council in 2025.”
‘EU needs comprehensive electricity storage strategy’
In a report published in March, consultancy LCP Delta and the European Association for Storage of Energy (EASE) similarly found annual installations had roughly doubled from 2023 to 2023.
However, with that report, the European Market Monitor on Energy Storage (EMMES) 7.0, giving its figures in gigawatt terms (power) rather than gigawatt-hours (energy) as SolarPower Europe’s did, direct comparisons are difficult.
EMMES 7.0 gave the total installed figure for 2023 at 10.1GW, making it the first time Europe’s storage installations on a GW-basis outpaced the US, which according to Wood Mackenzie totalled 8.7GW at all scales last year.
Both LCP Delta-EASE and SolarPower Europe’s reports converge on a takeaway that the residential sector in Europe far outpaces utility-scale and commercial and industrial (C&I) scale for storage adoption.
Around 70% of installed capacity came from home storage systems, about 21% from large-scale or utility systems and the remaining 9% in the C&I space, according to SolarPower Europe.
Many of those residential batteries were installed in Germany, the overall market leader in Europe with 5.9GWh of total deployments across all scales representing a 152% increase, while Italy was second with 3.7GWh (86% growth) and the UK, for a long time the leader due to its utility-scale front-of-the-meter (FTM) market slipping to third with 2.7GWh of installations, although it had a similarly big jump in deployments of 91%.
Although the EU has been seen to gradually recognise that it won’t get to its climate neutral target by 2050 without energy storage, more still needs to be done, the trade association said, echoing a recent call by its storage counterpart EASE.
The 60-page SolarPower Europe report, launched in the wake of the EU elections and ahead of Europe’s biggest solar and storage trade events, Intersolar Europe and ees Europe next week in Germany, is a call to action for policymakers as well as industry and regulators.
“While policymakers have focused on batteries for electrifying the automotive industry, their critical role in the green transition of the European power system has been largely overlooked. Flexibility through battery storage isn’t solely a technical matter for regulators and standardisation bodies; it demands immediate political attention and prioritisation,” SolarPower Europe director of market intelligence Michael Schmela said.
“The growth of renewables is reliant on the adoption of clean flexibility sources like batteries, essential for transportation and heating electrification, as well as grid modernisation. SolarPower Europe is calling for a comprehensive EU electricity storage strategy and a target of 200 GW by 2030.”
Next-generation sodium-sulfur battery storage: 20% lower cost, say BASF and NGK
It also has a cell degradation rate of less than 1% per year and an improved thermal management system that enables longer continuous discharge.
The two companies co-developed the new product, which they claimed enables a smaller footprint of containerised systems per installation and reduces maintenance costs.
Around 720MW/5,000MWh of NAS Battery systems have been deployed worldwide to date. Recently announced orders or projects include a 230MWh supply deal for a green hydrogen electrolysis cluster on the Baltic Shore of northern Germany, the battery tech’s first deployment in Eastern Europe with a 500kW/2,900kWh (5.8-hour duration) project in Bulgaria, a first-ever project deal in Australia and a 70MWh project in Japan which will enter energy trading markets.
The battery is designed to provide bulk storage of electricity for medium- to long-duration energy storage (LDES) applications requiring 6-hour storage or more. It operates at a temperature of 300°C, featuring a sulfur anode, sodium cathode and proprietary ceramic electrolyte.
The lack of degradation has long been one of its claimed key features, with no degradation expected for the first 15 years of an expected 20-year lifetime in the field for previous iterations, and an even better degradation profile claimed for the new MODEL L24 product launched earlier this week (10 June).
The new system is certified compliant with relevant energy storage industry safety standards including UL1973 and UL9540.
BASF has partnered with NGK to develop and market the NAS technology since 2019, marking the German chemicals company’s first entry into the energy storage market and closely followed by the formation of its BASF Stationary Energy Storage subsidiary.
NGK energy storage division VP and general manager Ryugo Takeda said the improvements come after an “intense and effective collaboration” between the two partners.
“The lower degradation rate of less than 1% per year is a remarkable result for the energy storage industry,” Takeda said.
“With the NAS MODEL L24 our customers will be able to reduce their initial investment in battery storage system as well as save on long-term project costs, approximately 20% over project lifetime,” Frank Prechtl, managing director of BASF Stationary Energy Storage said.
Read more Energy-Storage.news coverage of the NAS Battery.
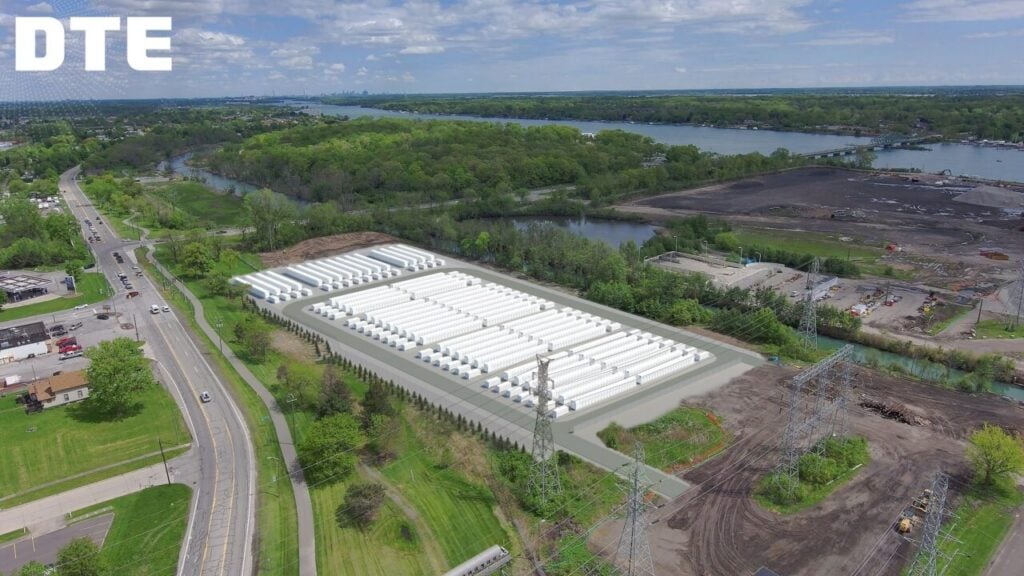
US utility DTE starts 220MW/880MWh BESS project at Michigan coal plant site
DTE Energy broke ground on the new 4-hour duration, 220MW (880MWh) BESS project on Monday (10 June).
The utility got the regulatory go-ahead from the Michigan Public Service Commission (MPSC) for the Trenton BESS project in March, as the stacks were finally demolished, as reported by Energy-Storage.news. At the time, the MPSC stated the expected cost of the project would be around US$460 million.
Commenting on the start of construction, state governor Gretchen Whitmer said that DTE “got this done with support from the Biden-Harris administration’s Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).”
According to the utility, the required Capex investment has been offset by US$140 million of incentives the company was able to avail of through the 2022 IRA legislation’s tax credits and provisions for infrastructure spending.
The battery storage system will charge with low-cost energy during off-peak times when renewable energy production is abundant, enabling DTE to manage its peak loads and accomodate more wind and solar on its grid.
‘Future is bright’
Whitmer’s state-level administration has also played a role in supporting Michigan’s energy storage sector as part of the governor’s Clean Energy Future Plan, passed in November 2023.
In addition to a 100% by 2040 clean energy target and carbon neutrality by 2050, making Michigan the first state in the US Midwest to commit to a net zero goal.
The package of five bills also saw the introduction of a 2.5GW energy storage procurement target for 2030. Michigan became the 10th US state with a storage policy target or goal, and led then-CEO of Key Capture Energy (KCE) Jeff Bishop to comment that it set a trailblazing pace for the Midwest region that others would likely follow.
Regional transmission operator (RTO) MISO incorporated electricity storage into its market portfolio in 2022, with rules that favour 4-hour duration projects like DTE Energy’s Trenton facility.
Illustrative rendering of how the project may look. Image: DTE Energy via LinkedIn
“Thanks to projects like today’s, strong federal leadership, and the Michigan Legislature’s clean energy and jobs package I signed into law last year, our future is bright,” Gretchen Whitmer said this week.
DTE Energy said the new BESS facility will help the utility integrate more renewable energy into its portfolio, in line with state goals and the company’s own 2022 integrated resource plan (IRP) which it dubbed ‘CleanVision’.
That includes adding 15,400MW of new renewable energy and 1,810MW of energy storage to its portfolio by 2042, on top of its existing 1,120MW of storage at the Ludington pumped hydro energy storage (PHES) plant, and 3,000MW of wind and solar capacity already existing or committed to prior to the 2022 IRP’s publication. That would bring its total renewable energy portfolio to 18,400MW and energy storage to 2,930MW by 2042.
The utility also said in its plan that it would be adding grid flexibility to integrate renewables capacity with new and emerging technologies for mid- to long-duration energy storage (LDES).
US firms NextEra and Entergy to deploy 4.5GW of solar and storage projects
“We’re excited about this joint development agreement, which will enable Entergy to provide our customers with low-cost, renewable energy as demand grows across Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi and Texas,” said Rod West, group president of utility operations for Entergy.
The two companies already have 1.7GW of renewable energy projects under development, and Entergy alone expects to add 2.9GW of new solar capacity by 2028. The company has also invested in co-located projects, with four solar-plus-wind projects in its pipeline, with a combined capacity of 4.9GW, which Entergy expects to commission by 2029.
NextEra, meanwhile, already has battery energy storage systems (BESS) in operation and development in 19 US states, including Arkansas and Texas, and reported strong growth in its solar portfolio in its 2023 financial reporting. The company added 1.2GW of new solar capacity in 2023, and posted net income of US$112 million in the fourth quarter of the year, and the new deal with Entergy will continue this expansion.
See the original version of this article on PV Tech.
CATL and Gotion deny forced labour in supply chain after US lawmakers call for immediate blocking of shipments
The letters were co-signed by Senator Marco Rubio and House of Representatives members John Moolenaar, Mark Green, Carlos Gimenez and Darin LaHood. The letters detailed numerous alleged ‘deep’ supply chain links between both CATL and Gotion to “the most troubling Chinese organisations involved in the enslavement of Uyghur Muslims in Xinjiang”, the committee said.
The letters called for the department to immediately blacklist CATL and Gotion and block shipments of their products into the US.
The two companies are major manufacturers of lithium-ion batteries as well as containerised battery energy storage system (BESS) units, with CATL the biggest in the world for batteries and one of the biggest for BESS.
CATL and Gotion deny allegations
In its response, CATL denied the allegations: “A June 5 letter by U.S. Members of Congress, accusing CATL of having connections to forced labor, is groundless and completely false. It cites information about suppliers in an inaccurate and misleading way.
“With some suppliers quoted in the letter, business relations ceased long ago. With other suppliers, business relations have been conducted with different subsidiaries and with absolutely no connection to forced labor or anything that violates U.S. applicable laws and regulations. With still others, we have never procured any products from them and the cited information is simply wrong and misguided.
“CATL is in strict compliance with all applicable laws and regulations with respect to its operations and business activities in the US”
Gotion meanwhile told Chinese state-owned outlet Yicai that the “claims were completely unfounded and absolutely wrong” and that it “has always respected human rights and protected the rights of employees”, the outlet reported today.
See the full Select Committee letters on CATL (here) and Gotion (here), and CATL’s full response (here).
Ramping up of existing trade war
The allegations come amidst a ratcheting up of protectionist measures by the US towards China, particularly in the clean energy technology space.
Last month, the US tripled import tariffs on lithium-ion battery imports from China (as well as solar technology and other industrial products) effective for battery energy storage systems (BESS) from 2026. The move, which garnered a mixed reaction from industry sources, will increase the cost of BESS in the US by 11-16% according to consultancy Clean Energy Associates.
And around the turn of 2023/24, a CATL BESS unit was disconnected at a US Marine Corps facility shortly before being removed entirely under pressure from US lawmakers who have accused CATL of being funded by and enjoying the support of the CCP.
In addition, CATL has recently tweaked its ownership structure to reduce its shareholding by executives that are also members of the CPP in order to mitigate against being a ‘Foreign Entity of Concern’ (FEOC), according to analysis by consultancy CRU Group. Being an FEOC would mean its cells would not be able to qualify for tax credit incentives under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 2nd Energy Storage Summit Asia, 9-10 July 2024 in Singapore. The event will help give clarity on this nascent, yet quickly growing market, bringing together a community of credible independent generators, policymakers, banks, funds, off-takers and technology providers. For more information, go to the website.
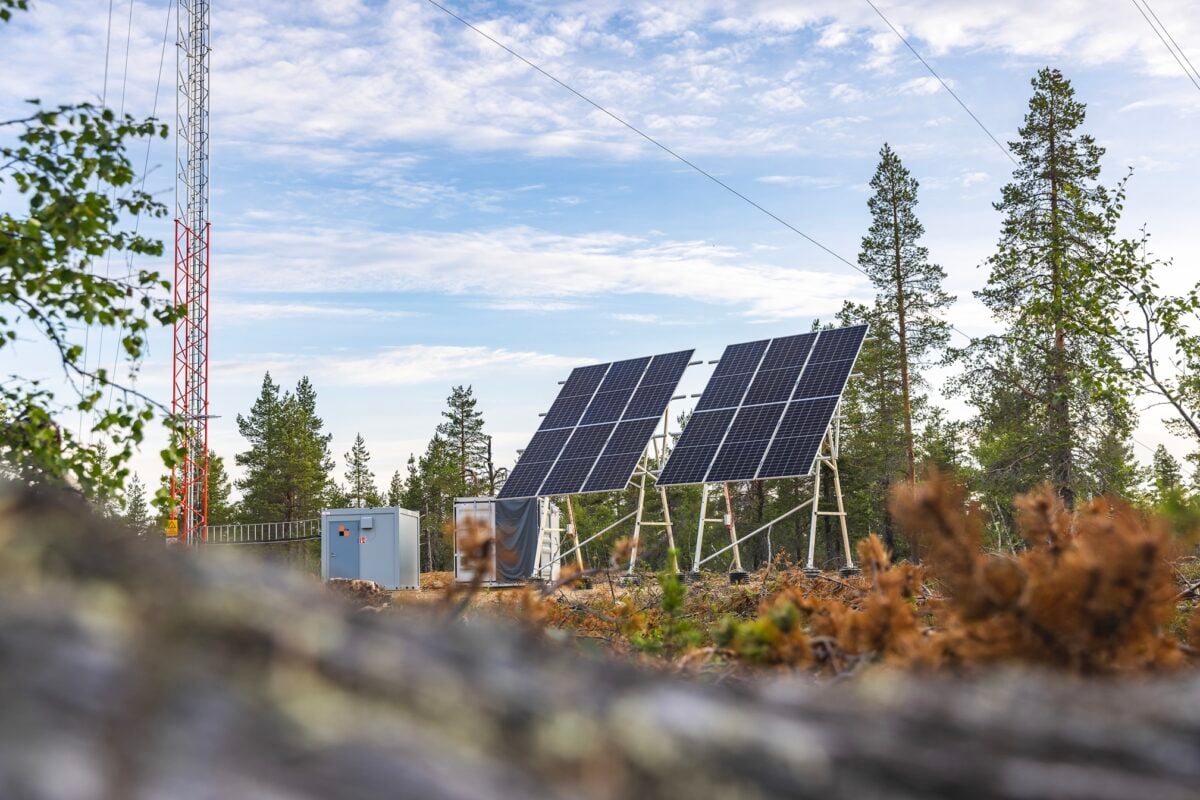
Finland: PV-plus-storage on telecom network plays into technology-neutral ancillary services market
The project follows a successful trial deployment by Elisa with Åland Islands-based telecoms provider Ålcom and local solar PV company Solel Åland.
In addition to supplying solar energy to power the mobile stations, the systems’ batteries can be used as backup power sources. At the same time, supplementary power can be bought from the grid, and Elisa’s Distributed Energy System (DES) technology will optimise the charging of the batteries to maximise cheaper purchases at off-peak times.
The DES solution also enables the batteries’ stored energy to be aggregated into a virtual power plant, accessing the Nordic grids’ frequency regulation ancillary services markets which have become an attractive opportunity for large-scale battery energy storage systems (BESS) with Sweden and Finland leading deployments, trailed by Denmark and Norway.
“This type of democratisation and real-time participation in the energy market has not been accessible to telecom operators before. Selling excess capacity back to the grid to help balance supply and demand can be a source of additional revenue for operators,” Elisa EVP for digital products and services Henri Korpi said in a press release.
Jukka-Pekka Salmenkaita, VP for artificial intelligence (AI) and the DES product at Elisa, told Energy-Storage.news that transmission system operators (TSOs) in the Nordic region “have opened up the electricity grid ancillary services market for technology-neutral competition.”
“This greatly facilitates VPP business cases while simultaneously encouraging new sources of flexibility capacity to enter the market, thus helping the electricity grid cope with large amounts of renewable production.”
15GWh of potential across Europe
Elisa has been bullish on the potential for combining batteries with telecoms stations for a while. When launching the DES solution late last year, a company spokesperson said that Europe-wide, there is scope for the deployment of 15GWh of energy storage at radio access network (RAN) stations.
The combination of the two technologies would also advance Europe’s decarbonisation and slash the costs of investing in clean energy technologies as well as telecoms infrastructure upgrades, the spokesperson said.
The launch of the DES solution came just under a year after Elisa received €3.9 million (US$4.17 million) funding from the Finnish government in February 2023 to develop the technology, stating at the time that the company would target deploying 150MWh of battery storage on its own networks, which it operates in Finland and Estonia.
Meanwhile, it is also working with third parties such as Ålcom and, in a previous deal, with Helsinki-based cellular infrastructure construction and maintenance provider DNA Tower.
Elisa’s Jukka-Pekka Salmenkaita noted, however, that Ålcom’s installation of the DES “is the first one that implemented VPP optimisation of locally produced solar energy,” with projects deployed until now only featuring batteries that charged from the grid.
From there, it has made the hybrid solar-plus-storage solution commercially available to other customers, and Elisa has said previously that it is open to taking the technology into markets elsewhere in Europe.
According to Salmenkaita, the DES can be flexibly dimensioned to meet different requirements from both solar PV and battery perspectives and is compatible with a “wide range” of battery and power electronics vendors’ equipment.
Ålcom head of network Peter Löfman said that for its project, lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries manufactured in Sweden by startup Polarium have been chosen. Löfman said the telecoms company’s preference had been for a European vendor.
Interestingly, while Elisa’s Salmenkaita said lithium iron phosphate (LFP) chemistry batteries are typically the most competitive for this type of application, the company is “closely monitoring the development of sodium-ion alternatives.”
Elisa was a winner at the 2023 Energy Storage Awards, hosted by our publisher Solar Media in September last year, in the category of Distributed Energy Storage Project of the Year.
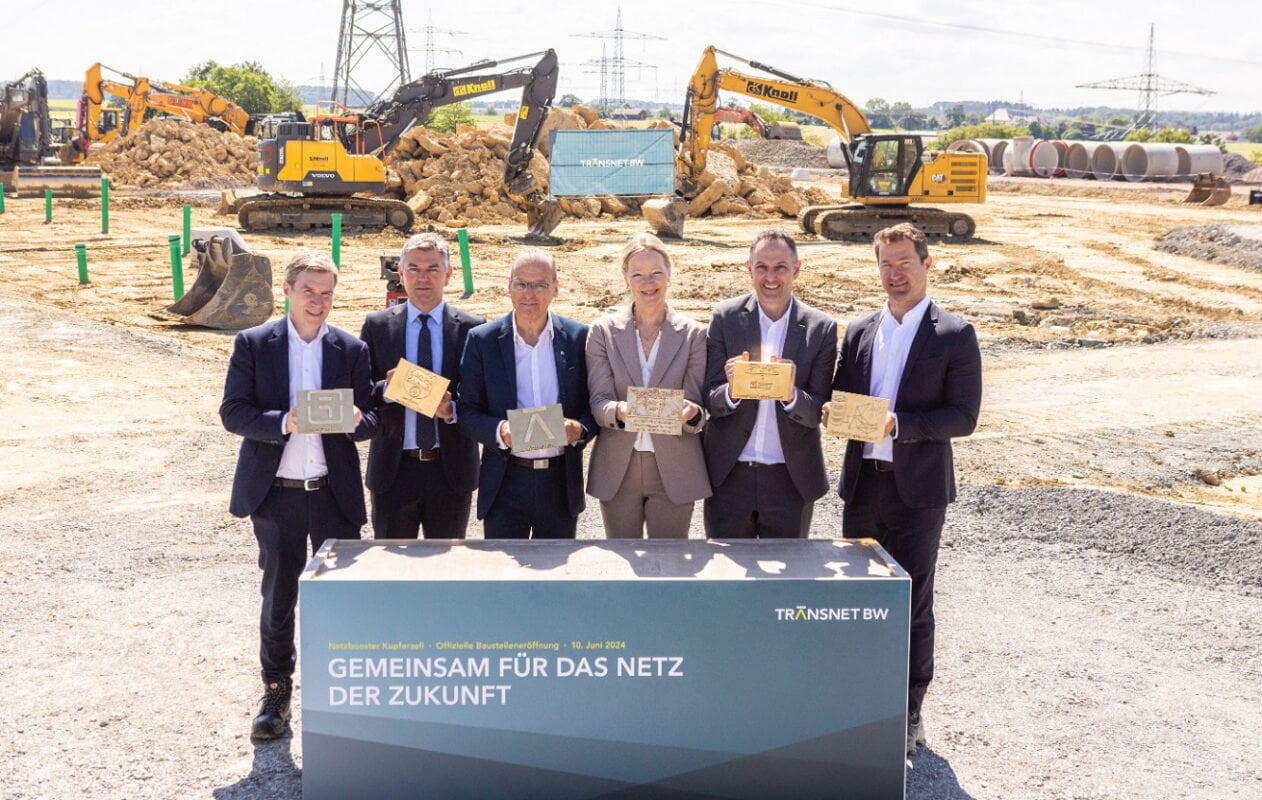
Fluence/TransnetBW Grid Booster breaks ground; EU funds LEAG’s hydrogen & flow battery project in Germany
The project in Kupferzell, Baden-Württemberg will act as a transmission asset for TransnetBW to operate the grid more efficiently, particularly in light of regional imbalances in Germany’s electricity system – renewable generation is predominantly in the north while demand centres are in the south.
A big part of that is mimicking the function of the extra long-distance, high-voltage lines which serve as a backup for primary lines, allowing for more use of those lines.
The project – Netzbooster in German – was approved by the regional council in April, allowing for construction to go ahead and for Fluence to start shipping BESS units.
Dr. Werner Götz, CEO and chairman of TransnetBW, said: “By using this technology in innovative ways we can increase capacity in the existing electricity grid and integrate more renewable energy. The Netzbooster is thus making an important contribution towards the energy transition.”
Grid Boosters are sometimes called storage-as-transmission or non-wires alternative (NWA) when at the smaller scale. Germany is the first country to launch such projects using BESS at scale, introducing the concept around five years, while similar projects have been deployed in Lithuania, Brazil, and some US states such as New York.
Fluence is also providing the BESS for two Grid Boosters from another of Germany’s four TSOs, TenneT, totalling 200MW while another TSO, Amprion, is deploying five totalling 250MW with the BESS provider not yet revealed.
EU puts €58 million towards LEAG’s hydrogen-plus-flow battery project
In similarly-timed news, the EU has provided a grant of €58 million (US$62 million) to coal and lignite power plant operator LEAG for a project that will combine green hydrogen and novel flow battery technology.
The funding is from the Just Transition Fund (EU JTF) and will go to LEAG’s ‘H2UB’ project. The project is aimed to building a centre for green hydrogen production paired with large-scale energy storage at its Boxberg power plant site.
In June last year, it tied up with NYSE-listed iron flow battery company ESS Inc to use the company’s proprietary technology for a 50MW/500MWh system as part of the project.
In the EU funding announcement, LEAG said the funding would go towards the hydrogen and ‘construction of a solid flow battery as a storage facility for electricity from renewable energies’ though it didn’t mention iron flow batteries or ESS Inc specifically.
In response to queries from Energy-Storage.news, LEAG said the ‘funding refers to parts of the H2UB Boxberg project’ while ESS Inc said the funding is not for its part of the project specifically but for the larger programme to combine hydrogen and energy storage at Boxberg.