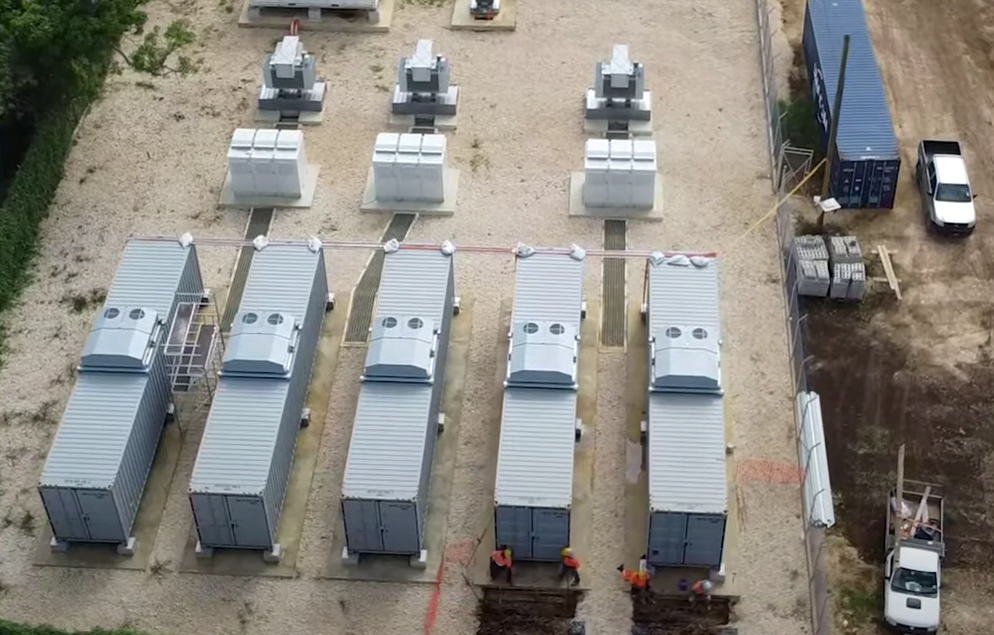
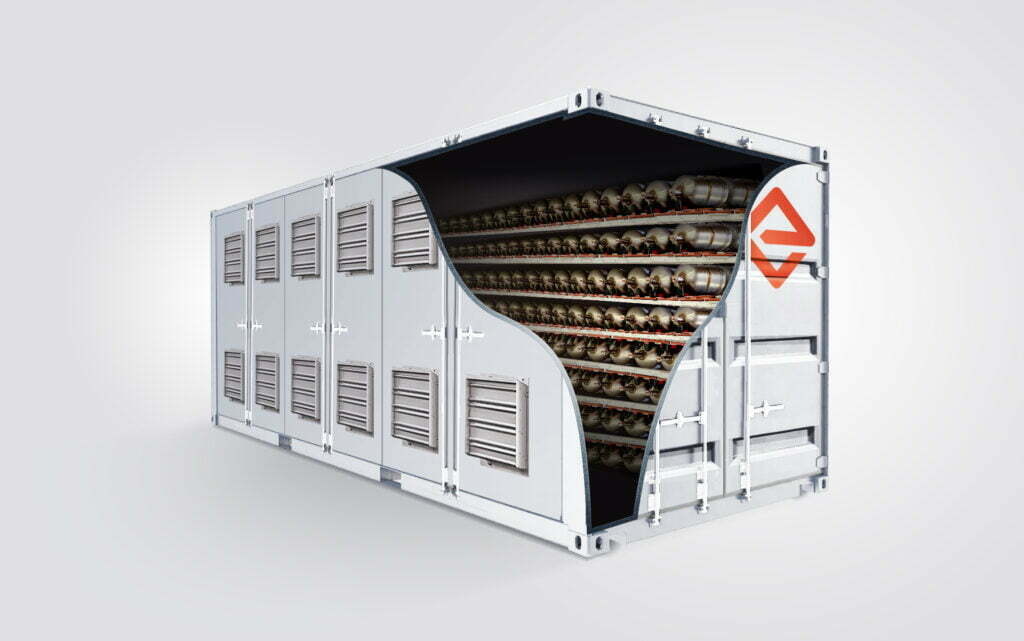
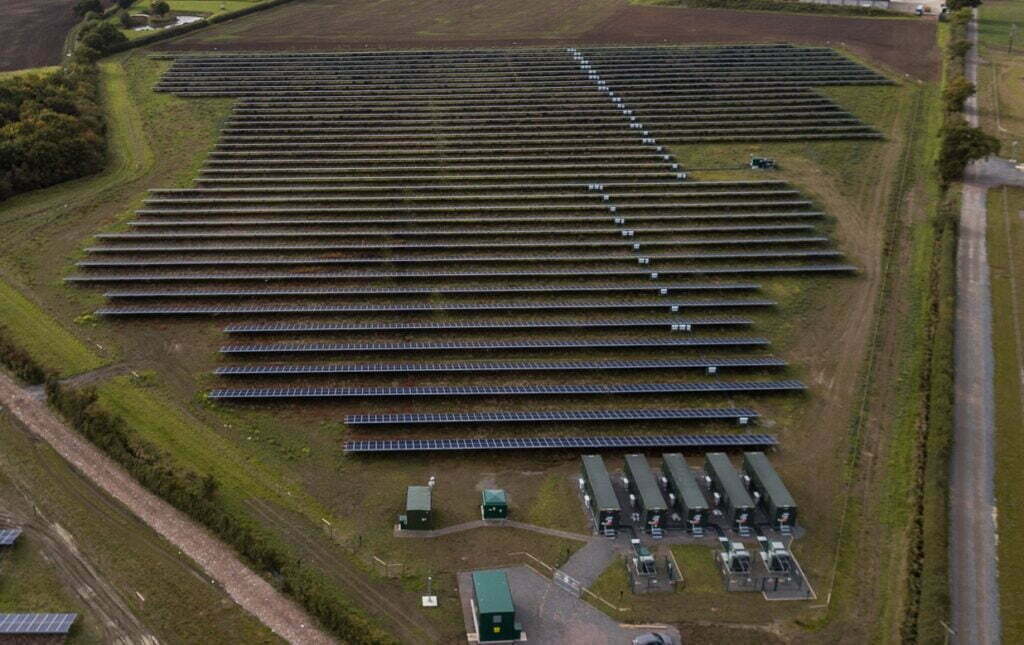
The battery energy storage system in Tonga. Image: Akuo corporate video screenshot.
French renewable power producer and developer Akuo Energy has commissioned a 29.2MWh battery energy storage system (BESS) in Tonga, several weeks after powering up a 19MWh project in Martinique.
The Tonga 1 and Tonga 2 storage systems are on Tongatapu, the main island in the archipelagic South Pacific nation, and connect to the grid of public operator Tonga Power Limited.
The two total 16.5MW of power and 29.2MWh of energy making this the largest BESS in the South Pacific, Akuo said. Both individual systems comprise Akuo’s Storage GEM modular containerised solution, three for Tonga 1 and five for Tonga 2.
Tonga 1 is a 9.3MW/5.3MWh designed to improve grid stability, with a duration of just 34 minutes. Tonga 2 is a 3.3-hour system with 7.2MW/23.9MWh of energy, designed primarily for load shifting.
They have already allowed Tonga to double its renewable energy capacity with the recent addition of 6MW in solar PV power, bringing the country’s renewable mix to around 20%. It aims for 70% by 2030.
The BESS also demonstrated its resilience during a tsunami in January which devastated the coastline and cut the country off from the outside world. The BESS continued operating and helped stabilise the grid in the days following the natural disaster.
The two projects totalled US$53 million in investment, of which 56% was from the UN’s Green Climate Fund, 23% from the Asian Development Bank, 10% from the Tongan government, 6% from Tonga Power and 5% from the Australian government.
Largest storage system in Martinique
The announcement comes a month after Akuo commissioned a 19MWh BESS on the French overseas territory of Martinique in the Caribbean, although the press release said its contractual effective volume is 12MWh.
The Madina Storage facility also uses Akuo’s Storage GEM containerised solutions and is a lithium-ion-based BESS (Akuo didn’t reveal the chemistry for the Tonga facility).
The BESS connected to the island’s grid, operated by French state-owned energy company EDF, will enable greater penetration of renewable energy. It will provide load shifting capabilities as well as grid frequency regulation services in the event of a sudden loss of power.
French commercial bank Groupe BPCE was the facility’s banking partner while listed investment firm Methanor provided it with equity financing.
Eric Scott, chairman and co-founder of Akuo, said: “We are very proud to put this storage facility into service, proof if it were necessary of the key role this technology plays in power networks’ performance and of its complementarity with the production of renewable energy.”
Akuo was founded in 2007 by the founders of Perfect Wind after they sold their entire wind portfolio to Spanish multinational electric utility Iberdrola. The company won solar tenders on French overseas territories last year and has invested €2.8 billion (US$3 billion) for a total capacity of 1.4GW renewabele energy capacity (operational or in development).
Continue reading