The energy storage division of New HOrizons Ahead (NHOA), which also has business lines for e-mobility and electric vehicle (EV) fast charging infrastructure, recorded a 384% growth in online BESS capacity at the end of Q3 2022 to the end of Q3 2023, as reported by Energy-Storage.news.
In an announcement made today (19 February), Eku Energy said it anticipates the BESS projects to be operational by the end of 2024. It is worth noting that Eku Energy already has a 40MW/40MWh battery in Maldon, Essex in construction.
The individual capacity of the BESS projects or output to the grid in megawatts was not disclosed.
The company now has 4.6GWh in development, construction and operation across the UK, Australia, Italy and Japan to deliver 9GWh by 2028.
Sandra Grauers Nilsson, CEO of Eku Energy said: “Breaking ground at Basildon and Loudwater is a major milestone for Eku Energy as we work to support the UK’s decarbonisation goals and expand our global footprint. We have an ambitious pipeline of battery storage projects which we are developing at pace and scale, and we are delighted to have partnered with NHOA Energy to advance the energy transition.”
To read the full version of this story, visit Solar Power Portal.
The evolving BESS market in 2024: A key year for safety, new technologies, and long-duration energy storage
The technology will continue to mature this year, and while there will be continued advancements in ESS, there will also be a greater focus on safety as energy storage becomes more commonplace and transitions from a novelty to a necessity. 2024 will also see an evolution in how BESS will be used in the future.
This article is going to elaborate on those three topics and will provide more details and the whys and hows of the developments in 2024.
The year of safety at scale
If the energy storage industry has learned anything from 2023, then it is that battery safety requires more attention.
Numerous incidents in 2023 show that keeping batteries safe is not as easy as it may seem in the beginning. Batteries are complex electrochemical systems. They require safety measures beyond regulatory compliance.
Their safety will no longer be viewed as just a box to be checked, but as an intrinsic element vital for the scalable and sustainable growth of battery technology. This paradigm shift recognises that as battery applications become more diverse and widespread, the margin for error narrows. A more comprehensive approach to safety is needed.
As part of this comprehensive approach, BESS providers and operators will focus increasingly on operational safety, highlighting the importance of continuous monitoring throughout the battery’s lifecycle, from commissioning to end-of-life (EoL).
Preparing batteries for testing. Image: TWAICE.
This approach underscores the dynamic nature of battery systems, where safety is not a static feature but a continuous requirement. Advanced monitoring systems and predictive maintenance technologies are being integrated into battery systems, enabling real-time tracking of performance metrics and early detection of potential safety issues.
This not only enhances the reliability of battery systems but also extends their operational lifespan, ensuring safety and efficiency throughout their use.
In essence, as the energy storage industry moves away from an early adopter phase to a more mature application of BESS, battery safety will be a key focus point. This is because battery safety and reliability play a crucial role in operating batteries in an efficient and scalable manner.
From sodium-ion to solid-state
Along with advancements in safety, BESS will also see innovative developments in technology this year. The BESS industry has been dominated by lithium-ion batteries, but the need for more long-duration storage, which cannot currently be done economically and safely with lithium, will open the door for promising non-lithium technologies.
Applications requiring extended storage durations, particularly those exceeding 8 hours, will be increasingly using sodium-ion batteries, for example. This is due to the demand for more economical storage solutions.
This shift is driven by the characteristics of sodium-ion technology, which offers a balance of affordability, safety, and suitable energy density for long-duration storage. Its chemistry is particularly advantageous for stationary applications where space and weight constraints are less critical than in mobile applications.
Sodium-ion batteries have a significant cost advantage compared to lithium-ion batteries, as sodium can be extracted practically anywhere in the world.
Simultaneously, solid-state batteries will emerge as a premium option in the market. Solid-state batteries are recognised for their superior performance, including higher energy density and enhanced safety features due to their non-flammable solid electrolytes.
However, this advanced technology comes with higher costs, positioning solid-state batteries as a luxury choice in the battery market, at least until technology matures. Solid-state batteries require sophisticated manufacturing processes and new supply chains making production expensive.
Despite the cost, the demand for solid-state batteries will be growing, particularly among applications where performance and safety are paramount, and budget constraints are less of an issue.
This trend highlights a diversifying battery market, where different technologies are being optimised for specific use cases, offering solutions ranging from cost-effective to performance-oriented.
The application-led evolution of BESS
In 2024, one of the most notable developments will be the extended duration capabilities of large-scale batteries. Some systems will reach up to 4 hours of continuous operation. This extension in duration represents a major step forward in energy storage, enabling more effective integration of renewable energy sources into the grid and providing greater stability in energy supply.
The growing demand for long-duration energy storage (LDES), lower-power-density applications will be particularly evident in sectors where energy needs are substantial but spread out over longer periods. This includes industrial processes, large-scale renewable integration, and grid stabilisation in areas with intermittent power sources. The focus on long-duration storage reflects a broader shift in the energy industry towards more diverse and reliable energy solutions.
Alongside these technological advancements, there will be a shift in the economic landscape of BESS. Operators are now exploring additional revenue streams, commonly referred to as ‘revenue stacking’.
This involves leveraging the multifaceted capabilities of storage systems to participate in various market services like peak shaving, load shifting, frequency regulation, and black start services.
However, this diversification of revenue sources comes at the cost of increased operational complexity. Managing these different revenue streams requires sophisticated control systems, a deep understanding of the market dynamics and the knowledge of how different load profiles impact battery degradation. All of this makes the operation of BESS assets more intricate than ever before.
In summary, the evolution of BESS in 2024 is characterised by several key trends: a continued focus on safety, the commercialisation of non-lithium technologies, the extension of battery durations for large-scale systems, and the exploration of additional revenue streams through complex operational strategies. These trends underscore the dynamic nature of the BESS market and highlight the ongoing innovation and adaptation in response to changing energy needs and market opportunities.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 9th annual Energy Storage Summit EU in London, 20-21 February 2024. This year it is moving to a larger venue, bringing together Europe’s leading investors, policymakers, developers, utilities, energy buyers and service providers all in one place. Visit the official site for more info.
About the Author
Dr. Matthias Simolka is a product manager and part of Technical Solution Engineering at TWAICE, a cloud-based battery analytics software provider headquartered in Germany. Matthias bridges the gap between Sales, Product and Tech, working with all teams to ensure maximum value and the optimal solution is delivered to battery customers.
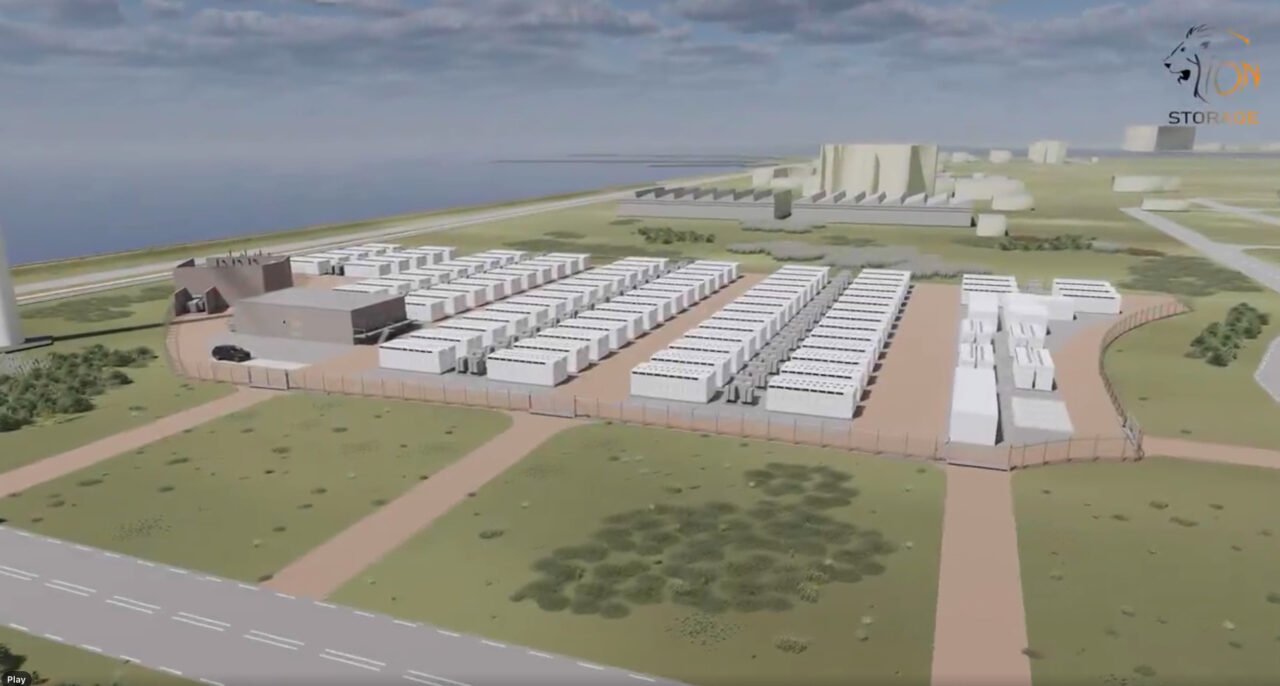
Dutch developer Lion Storage planning 1.5GWh BESS for 2026 operation
Like the country’s two largest operational BESS projects, it will be located in the Vlissingen port area, one of the Netherlands’ new ‘energy hubs’, Lion Storage said. Energy-Storage.news interviewed the owner of both of those projects, SemperPower, recently for a Premium article.
Lion said the location gives it direct access to the high-voltage network operated by the country’s transmission system operator TenneT.
Energy-Storage.news has asked the company what progress has been made on the Mufasa project, considering it has been listed on its website for over a year with the same commercial operation date, and will update this article when a response is received.
Announcing the news on Linkedin, Lion Storage said: “Operating on a full merchant basis, Mufasa will be active in all wholesale power and ancillary services markets, facilitating further integration of renewable power on the power grid, while offering system services ensuring system balance, grid stability and long term security of supply.”
We interviewed Lion’s CTO Jeroen Althoff at the Energy Storage Summit EU last year, at which he discussed the company’s plans and the major challenges in the Netherlands’ energy storage market.
A render of the Mufasa project on Linkedin showed it being comprised of Tesla Megapacks.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 9th annual Energy Storage Summit EU in London, starting tomorrow: 20-21 February 2024. This year it is in a larger venue, bringing together Europe’s leading investors, policymakers, developers, utilities, energy buyers and service providers all in one place. Visit the official site for more info.
Brookfield’s X-ELIO invests in German battery storage firm Eco Stor
Eco Stor is a battery storage project developer and battery energy storage system (BESS) integrator. After this deal, X-ELIO, NIC, company management and ‘certain existing shareholders’ will continue to invest in progressing the company’s BESS project pipeline in Germany, which totals 6GW.
This does not appear to be a full sell-down by A Energy (through Agder Energi Venture), however, with Eco Stor CEO Trygve Burchardt commenting: “We are very pleased to now announce that X-ELIO and NIC will be investing in ECO STOR together with the continued support from Å Energy.”
It comes a few weeks after another German BESS developer, Kyon Energy, was acquired by oil and gas major TotalEnergies. Kyon and Eco Stor have partnered on projects in the past.
It grows X-ELIO’s energy storage market presence into Germany, with assets under construction, operation or fully permitted for construction in Australia, Chile and the US. Global infrastructure investment firm Brookfield has been 100% owner of X-ELIO since March 2023.
For NIC, the deal grows its presence in the German clean energy market after it acquired 100% of solar PV project developer MaxSolar in 2022.
Read all Energy-Storage.news’ coverage of the German energy storage market here, including the launch of the government’s Energy Storage Strategy and the start of construction at what has been claimed as the country’s largest BESS.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 9th annual Energy Storage Summit EU in London, 20-21 February 2024. This year it is moving to a larger venue, bringing together Europe’s leading investors, policymakers, developers, utilities, energy buyers and service providers all in one place. Visit the official site for more info.
Friday Briefing: No nostalgia for ‘The New Normal’ but the BESS market remembers all
It is pretty much sold out despite being at a much bigger venue this year, so you can understand that it’s been rather hectic for our brilliant and hardworking team.
Meanwhile, our publishing division is putting the finishing touches to Volume 38 of PV Tech Power, the quarterly journal for the downstream solar PV sector to which Energy-Storage.news contributes the Storage & Smart Power section. It is, of course, included in your subscription to ESN Premium.
A lot to do but more importantly, a lot to look forward to.
But before we get to that, today’s Friday Briefing gives us the perfect opportunity to instead look back on the Energy Storage Summit 2021 and get a fascinating snapshot of where some of us were back then, and what we thought we’d see in the market by, well, now.
It’s unlikely many of us look back on the second year of the global pandemic and the human cost of lives and productivity lost or damaged with great fondness. As a much more minor consideration than that, I expect not many of us miss what was euphemistically described as “the new normal” of cancelled conferences hosted online instead of in person.
But, actually, the industry – and again, the Solar Energy Events team – did a great job even then. One silver lining is that the 2021 edition’s live streamed sessions are all available on the Solar Energy Events team’s YouTube channel.
I was privileged and honoured to be asked to moderate the keynote panel discussion which opened the event, and its participants included representatives from Gore Street Capital and Gresham House. They were at the time, managers of the UK’s two listed funds dedicated to investing in large-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) assets, since joined by Harmony Energy Income Trust to make three.
One of the big topics at that time, which feels pretty relevant to think about today as well, was that the market was mid-shift towards revenue stacks that were more focused on merchant risk than on contracted revenues.
“Generally, from our perspective, we think that it’s true, and it’s definitely going to be the case, that future stacks and revenue streams will be very different for batteries than they are now,” Alicia Kowalewska-Montfort, Gore Street Energy Storage Fund project manager said.
Kowalewska-Montfort referred to a period towards the end of 2020 and beginning of 2021 when huge price spikes resulted in some prices in the market reaching £4,000 (around US$5,500 at that time)/MW/hr. That was, she said, a “small sample” that nonetheless indicated that the direction of travel towards increased renewables on the grid, and therefore increased volatility, would create more and more viable opportunities for storage.
Anyone accurately predicting the business case for BESS assets 20-25 years down the line would have to be a magician or fortune-teller, the project manager said. However, the overall thesis Gore Street held was that wholesale energy trading would play an increasingly large layer of the revenue stack, with ancillary services revenues as the “baseline”.
Gresham House fund manager Ben Guest said that with the growing importance of trading on the horizon, Gresham House was looking to incrementally increase the duration of its assets – which was, of course, referred to as an ongoing piece in the fund’s recent financial update a couple of weeks ago.
“Ultimately, the ancillary services market is much smaller than the deeper energy markets. But I agree with Alicia, which is that it’s difficult to know when trading becomes very profitable,” Guest said.
“There are some very, very good guideposts, which [are from] simply analysing the change in the generation mix, and therefore in the merit order.”
As we heard from Henry Easterbrook of developer Fig Power in our recent webinar on merchant risk, Guest said two years earlier that it’s the fate of natural gas in the Great Britain (GB) electricity market which might most clearly decide just how much battery capacity, and at what duration, will be playing into wholesale markets.
You can watch the opening keynote panel: ‘What is the Key to Really Making Money from Batteries?’ below and you can indeed also watch the rest of the event’s great sessions – and lots of other content – on the event team’s channel here.
It includes lots of great content and speakers, by no means limited to the UK market alone, so we’d highly recommend having a browse.
[embedded content]
We very much hope to see you at next week’s Summit, part of our industry-leading series of global conferences. Look out for news and exclusive interviews from the show in the coming weeks.
In other stuff to look forward to on ESN Premium, join us early in the week for an exclusive interview with advanced compressed air energy storage (A-CAES) company Hydrostor.
Here’s what that article’s author, Cameron Murray, Energy-Storage.news senior reporter, has to say about that:
“The Canada-headquartered company is often described as a compressed air energy storage technology A-CAES firm, but Hydrostor president Norman told us it would be more apt to call it a system integrator and, currently, it’s just as busy doing project development.
The approach is different to most other long-duration energy storage (LDES) technology firms, which tend to just provide technology for other companies’ projects. But, whether it remains that way long-term is an open question, and one Norman discussed for the interview.”
Happy Friday!
Friday recap: This week on ESN Premium
In case you missed them… click the headlines to read the following Energy-Storage.news Premium articles:
Transferability ITC deals for 1GWh+ of US battery storage: ‘market has grown faster than anyone expected’
Blackstone and Foss & Company have completed transferability investment tax credit (ITC) deals for BESS projects in California and Texas, a market that has grown “faster than anyone expected” according to tax credit ecosystem Crux.
sonnen CEO: ‘We gained credibility in the US through Utah virtual power plant’
Utah is not perhaps a US state people would immediately associate with cutting-edge clean energy tech development, but that’s where sonnen’s virtual power plant (VPP) offering took shape.
Illinois BESS project owner seeking damages from LG for ‘defective’ supplied batteries
The owner of a battery energy storage system (BESS) project in Illinois, US, is seeking at least US$10 million in damages from LG Energy Solution for supplying allegedly defective batteries, a court document shows.
Energy storage tax credits in US priced highest among all clean energy types
Energy storage investment tax credits (ITC) were priced more highly than any other clean energy type in transferability transactions last year, according to a report from tax credit ecosystem Crux which its CEO discussed with Energy-Storage.news.
Energy storage tax credits in US priced highest among all clean energy types
Crux CEO Alfred Johnson: “The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) saw that additional supply of capital would be needed for the clean energy sector and this was aimed at doing that.”
Although transferability became effective on 1 January, 2023, it was only after the IRS clarified how to use it in June 2023 that deals could happen, and the market took off between August and the end of the year, Johnson said.
The company estimates that there were between US$7-9 billion in tax credit transactions using transferability done by the end of the year across clean energy in the US, already one-third or even half of the size of the traditional tax equity market of US$20 billion.
Crux’ estimate covers investment tax credits (ITC) and production tax credits (PTC), the latter of which includes both the production of electricity from a renewable energy plant like solar or wind, and the output of a clean energy manufacturing plant like a lithium-ion gigafactory or PV module factory.
As we reported in an article earlier this week, Johnson said that the transferability market has taken off far quicker than anyone expected and had certainly broadened the pool of investors. The majority of deals were also under US$50 million, typically not a deal size that would have access to traditional tax equity investment.
Solar PV took the largest share of the deal pie followed by the 45x PTC for advanced manufacturing, a big chunk of which was a US$700 million deal struck by PV module manufacturer First Solar with finance tech firm Fiserv.
“That indicates that there is a broader market for more types of technologies at better prices than what was previously anticipated in the market,” Johnson said.
Energy storage priced the highest of all tax credit deals through transferability
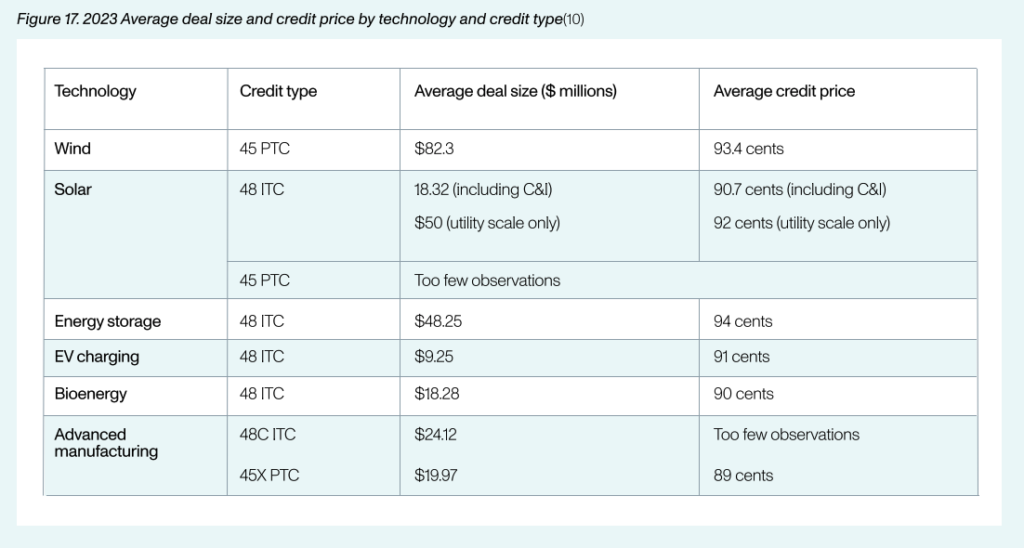
Through the firm’s marketplace, which provides deal intermediaries with information on transferability deals, Crux has been able to break down the transferability market to-date down to granular detail. This includes the differing prices tax credit buyers are paying for ITCs or PTCs depending on the technology type, shown in the table below.
The ITC for standalone energy storage was the highest priced of all types, at US$0.94 on the dollar versus US$0.89-93.4 for other types. That means buyers of standalone energy storage ITC paid more than any other type of ITC or PTC.
Johnson said this was primarily due to a larger average deal size for standalone energy storage projects at US$48.25 million than most technologies and the higher price that buyers would subsequently need to pay sellers.
Source: Crux 2023 TTC Market Intelligence Report
However, utility-scale solar ITCs were priced at US$0.92 and wind PTCs were priced at US$0.934 despite both seeing larger average deal sizes (US$50 million and US$82.3 million respectively).
So storage could still be seen to have outperformed despite some industry sources saying last year that it might take some time for the tax equity community to get comfortable with standalone energy storage. One delegate at the Energy Storage Summit USA last year said they agreed to sell their project’s standalone ITC for just US$0.85. Note that this was prior to the IRS’ guidance on transferability.
“The storage projects where ITCs were transferred were larger projects being built by more established players. Storage was also often bundled with wind and solar in tax equity deals prior to transferability so it is not an asset that the market is unfamiliar with,” Johnson said.
A lack of wind ITC deals was primarily because most projects in the pipeline have already had their financing secured prior to transferability, meaning no need for additional deals needed to get them built.
See the Crux’s full report here.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 5th Energy Storage Summit USA, 19-20 March 2024 in Austin, Texas. Featuring a packed programme of panels, presentations and fireside chats from industry leaders focusing on accelerating the market for energy storage across the country. For more information, go to the website.
US project financing roundup: SMT Energy, UBS, Plus Power, Available Power strike deals
The investment came from Greenprint Capital Management, and will help the project reach a commercial operation in Spring 2024.
It comes a few months after Plus Power secured a US$1.8 billion financing package for five BESS projects in ERCOT and Arizona, totalling nearly 3GWh of energy storage, which executive chairman Brandon Keefe told Energy-Storage.news showed it was “…driving energy storage into the mainstream of capital markets”.
SMT Energy sells 400MW of ERCOT BESS to UBS
In related ERCOT news, developer SMT Energy has sold 400MW of BESS projects in the state to UBS Asset Management, which will come online over the course of 2024 and 2025.
SMT Energy said the firm has now developed over US$1.5 billion of BESS projects in the US and operates one of the largest portfolios in the country. It recently sold a portfolio of 10 projects, also in ERCOT, to investor SUSI Partners.
CleanCapital and Available Power agree JV for US BESS development
Investor CleanCapital and BESS developer Available Power have formed a joint venture (JV) to develop BESS projects across the US.
The co-operation will see CleanCapital provide project financing, development, and construction expertise while Available Power will provide market insights, technology, and engineering expertise to develop the projects.
The announcement didn’t specify where the projects would be. Available Power has been active in the ERCOT market, which the firm’s VP business development Alex Krass discussed at last year’s Energy Storage Summit USA, put on by our publisher Solar Media.
It’s not clear how much BESS the pair plan to develop, but CleanCapital said it has a near-term pipeline exceeding 500MWh.
Solvent Energy enlists investment bank to explore sale of 3.6GW solar and storage portfolio
Developer Solvent Energy has hired Fifth Third Securities as financial advisor to explore the monetising of a large solar and storage portfolio, also in ERCOT, which could include a sale of projects at the ready-to-build (RTB) stage.
The 15 projects have a combined capacity of 3.6GW comprise of three solar-plus-storage projects and 12 standalone energy storage ones. Among these is the 200MW solar, 400MW/800MWh BESS Forts Trail project which has already reached RTB in 2023, while the rest of the projects are targeting RTB this year.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 5th Energy Storage Summit USA, 19-20 March 2024 in Austin, Texas. Featuring a packed programme of panels, presentations and fireside chats from industry leaders focusing on accelerating the market for energy storage across the country. For more information, go to the website.
Greece: Second round winners in BESS auction revealed
Various Greek and regional European news outlets have in the past 24 hours reported that that list of 48 projects has since been whittled down to 11 winning projects totalling nearly 300MW of capacity.
The process has seen project developers bid for long-term operating grants for their projects with the lowest bids winning, and it follows the first round in August 2023 which awarded a weight average of €49,748 (US$53,589) per MW per year to 12 winning projects totalling 411MW.
Another round is expected in Spring, which will award a further 300MW bringing the total to 1GW. The programme is backed by EU money, through the bloc-wide Recovery and Resilience Plan aimed at mitigating the negative economic effects of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Winning developers in the latest round are reportedly CNI Energy, Terna Energy (part of the Italy’s grid operator Terna), Heron, Amber Energy, Motor Oil, Energeiaki Techniki, Faria Energy and Enel Green Power Hellas, part of the Italy-headquartered international utility and independent power producer (IPP) Enel.
The weight average winning bid in this round was €46,680/MW/year.
Research firm LCP Delta wrote a deep-dive into the dynamics which would play out in the second round for Energy-Storage.news in September.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 9th annual Energy Storage Summit EU in London, 20-21 February 2024. This year it is moving to a larger venue, bringing together Europe’s leading investors, policymakers, developers, utilities, energy buyers and service providers all in one place. Visit the official site for more info.
Continue readingWärtsilä’s high energy BESS solution to get first field deployment at 600MWh Scotland project
Located in Kilmarnock, around 26 miles from the metropolitan area of Glasgow, it will be aimed at helping integrate growing shares of wind energy onto the grid. Construction began on the asset in January and it is scheduled for completion by the end of next year.
While the involvement of the Energy Storage & Optimisation (ES&O) arm of Finnish engine power plant and marine propulsion group Wärtsilä was already announced by Zenobē last month along with the closing of £147 million (US$184.46 million) financing towards the project – as reported by Energy-Storage.news at the time – more details were given today on the technology and the applications it will serve.
System operator’s Stability Pathfinders initiative
One notable aspect in that regard is that the project has received some funding from National Grid ESO, electricity system operator for the grid in Great Britain (GB), due to the key role it will play in helping stabilise the grid.
The ESO was spun out from the transmission system operator (TSO) National Grid as a separate entity a few years back, and while the TSO is tasked with maintaining the physical grid infrastructure, National Grid ESO’s job is to maintain the electric system’s reliability and security of supply on a day-to-day basis.
As part of that, the ESO’s Network Options Assessment (NOA) decides where investment into reinforcing the system should be directed, including what sorts of technologies, as well as geographical or grid node locations.
Zenobē’s Kilmarnock South BESS has been designated as an NOA Stability Pathfinder project, as it will help support the operation of the grid as it transitions away from reliance on thermal power generation from fossil fuels and nuclear energy towards renewables.
The decline of thermal generation and increasing uptake of variable renewable energy (VRE) means that inertia on the grid, traditionally provided as a sort of by-product of the rotation of turbines, has decreased. Inverter-based resources such as wind, solar and the power conversion system (PCS) equipment in BESS assets can instead provide that inertia synthetically through advanced upgrades of the inverters.
That’s been seen in Australia, where the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) has issued grants to large-scale battery projects that add advanced inverters either at design stage or as retrofits, including Wärtsilä’s recently completed 250MW Torrens Island BESS for utility AGL in South Australia.
At the same time, Zenobē’s 300MW BESS will help reduce the curtailment of wind energy going to the grid, an expensive problem for the UK and other countries that have rapidly gone to higher shares of renewables.
Higher energy density
Wärtsilä launched its GridSolv Quantum High Energy (Quantum HE) in November last year, touting its use of 306Ah lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cells which enable 9% higher energy density than the previous iteration of its GridSolv Quantum solution.
Increased energy densities of both battery cells and complete systems have become a major trend in the industry recently, from the perspective of manufacturers, integrators and customers.
It also has improved safety features, the company said. Wärtsilä has been keen to emphasise the need for fire safety to be treated as a major priority for the industry for some time, claiming for example that the large-scale fire testing it subjects its products to sets a standard for worst-case scenario planning that should be a part of industry best practices.
As with all previous iterations of Wärtsilä’s BESS technologies, it will run on the company’s GEMS energy management platform, which Wärtsilä claimed will best enable the Kilmarnock asset to access market opportunities for owner-investor Zenobē.
It is also Wärtsilä’s second contracted battery storage project in Scotland, and its second in the country with Zenobē. The first, announced in Q1 2023, was the 200MW/400MWh Black Hillock project which is aimed to go online by the autumn of this year.
Wärtsilä ES&O chief Andy Tang said the company’s UK portfolio now exceeds 2GWh of storage capacity. ES&O enjoyed a 20% increase in sales and a 31% increase in order intake year-on-year from 2022 to 2023, and is now profitable. Parent company Wärtsilä is currently mulling its options for the future of the division, including seeking additional investors and divestment.
Zenobē Energy was a winner of two trophies including Developer of the Year at the Energy Storage Awards 2023. It also attracted more venture capital (VC) funding than any other company in the energy storage space globally during last year, according to research group Mercom.
Zenobē head of commercial products Charles Pearce appeared on a recent Energy-Storage.news webinar, sponsored by energy storage trading and optimisation specialist GridBeyond, discussing the appetite of investors in the UK BESS market for merchant risk versus contracted revenues.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 9th annual Energy Storage Summit EU in London, 20-21 February 2024. This year it is moving to a larger venue, bringing together Europe’s leading investors, policymakers, developers, utilities, energy buyers and service providers all in one place. Visit the official site for more info.
RWE completes 360MWh of US BESS as ‘industry bounces back’
All three are co-located with solar PV projects. Bright Arrow is a 100MW/200MWh BESS and 300MWac PV project in Sulphur Springs, while Big Star is an 80MW/120MWh system paired with a 200MW PV project in Bastrop County, both in Texas. In Arizona, it has brought online the 10/40MWh BESS, 52.5MWac PV Mesquite 4 project.
The Texas BESS projects will participate in the state’s electricity market, operated by ERCOT, while the PV output will be provided to specific companies (utility NRG Energy for Bright Arrow and an undisclosed company for Big Star).
For Mesquite 4, both the BESS and solar output will be provided to utility Modesto Irrigation District (MID). The project is part of a larger one called Mesquite Complex which now has a solar capacity of 530MWac.
ERCOT is the most active US state for BESS deployments along with California, though could overtake the latter’s roughly 7GW of grid-scale BESS when it hits 9.5GW in October this year (ERCOT’s own forecast). Projects are capitalising on a substantial ancillary service market as well as wholesale energy trading opportunities.
In Arizona, the market has been driven by long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs) or ‘tolling agreements’ where all of a BESS project’s offtake will be secured by a utility on a 10 or 15-year basis. This means projects there are mostly at the larger scale, including a 1GWh system on which Strata Clean Energy started construction last month.
“Battery storage is growing even more critical to enable the rapid deployment of wind and solar projects, help stabilize the U.S. power grid and better ensure that enough electric supply is available to meet demand,” said Andrew Flanagan, CEO of RWE Clean Energy, the firm’s US renewables arm.
BESS industry ‘has bounced back’ after 2022 challenges
Writing an article for the upcoming edition (38) of PV Tech Power, Solar Media’s quarterly journal for the downstream solar and storage industries, RWE Clean Energy’s director of BESS project design Swetha Sundaram detailed how the industry has bounced back after the challenges of 2022.
On a short-term basis this has been driven by BESS prices falling back down to expected trajectories while at the macro level, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and a growing familiarity with its provisions has been the major contributing factor.
Supply chain issues around balance of plant (BOP) equipment are still a major challenge, which Sundaram details in the article as well as the latest on grid-interconnection wait times.
Planning is now the name of the game for building projects, Sundaram says: “The BESS market landscape is more competitive than ever. To build projects economically and achieve the target COD, developers need to plan to procure equipment smartly, forge strategic partnerships to secure production volumes for battery systems and take into consideration domestic manufacturing, although it remains to be seen how much of the touted domestic manufacturing will take shape in time to feed the enormous North American battery market.”
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 5th Energy Storage Summit USA, 19-20 March 2024 in Austin, Texas. Featuring a packed programme of panels, presentations and fireside chats from industry leaders focusing on accelerating the market for energy storage across the country. For more information, go to the website.