When the firm raised €2.5 million back in November 2022, it presented itself as primarily repurposing used batteries from Tesla electric vehicles (EVs) into stationary BESS, otherwise known as second life energy storage. However, founder and CEO Oskari Jaakkola says that falls in the prices of new lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries since then have changed this.
“Due to the significantly increased cost competitiveness of first life LFP cells, our production is currently about 80-90% first life and we expect the trend to continue,” Jaakkola said.
Elaborating on this, he said: “At this moment, first life LFP cells are very attractive due to their longevity and price. However, we are agnostic in terms of battery chemistry and should another attractive technology emerge, we will evaluate it.”
“Second life cells are fit for purpose when it comes to battery energy storage. However, when looking strictly at cost, first life LFP is currently more attractive. There are other aspects supporting second life cells, such as ESG views and that’s why we want to keep the second life product in our offering and allow the clients to make the choice.”
The high cost of new lithium-ion batteries was often cited as a driver of the second life energy storage market when Energy-Storage.news spoke to companies throughout 2022 (interviews which culminated in a special feature on second-life energy storage in an edition of our quarterly journal PV Tech Power).
Cactos Fleet is targeting €70 million in capital, half equity half debt, and was set up to separate the long-term leasing and operation of BESS assets with the technology business of Cactos, activities which have different typical investor profiles.
Explaining the company’s business model and how it ties in to the decision to currently focus on first life LFP cells, Jaakkola said:
“Our product is smart energy storage systems as a service – we provide our clients with an all-inclusive service and the client only pays a monthly bill. We develop the technologies (both hardware and software), we assemble the BESS’s, we install, commission, maintain, trade and finance the systems. We also typically earn a performance-based fee and hence have a vested interest with our clients in making our BESS’s the most reliable, profitable and cost-effective products in the market.”
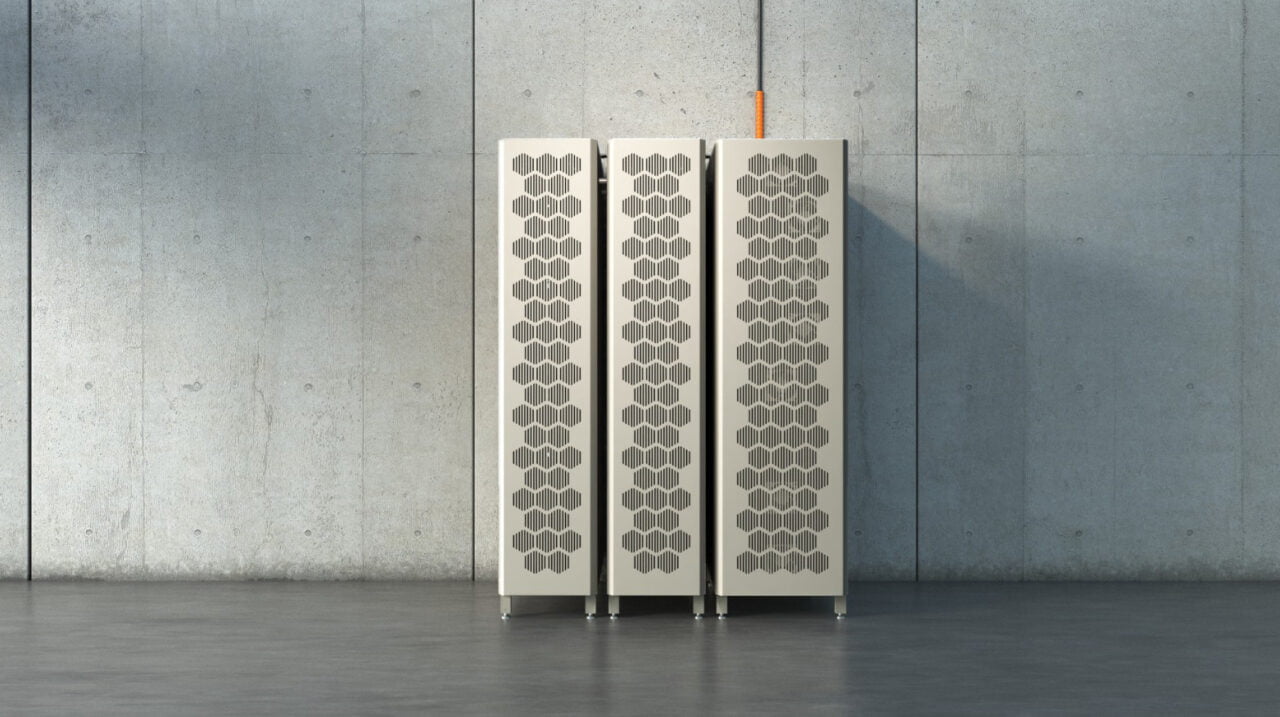
The firm’s first life BESS product is the Cactos One Cardo while its product comprising second life Tesla batteries is the Cactos One Classic. Its deployed BESS units are aggregated into a virtual power plant (VPP) using its proprietary software Cactos Spine.
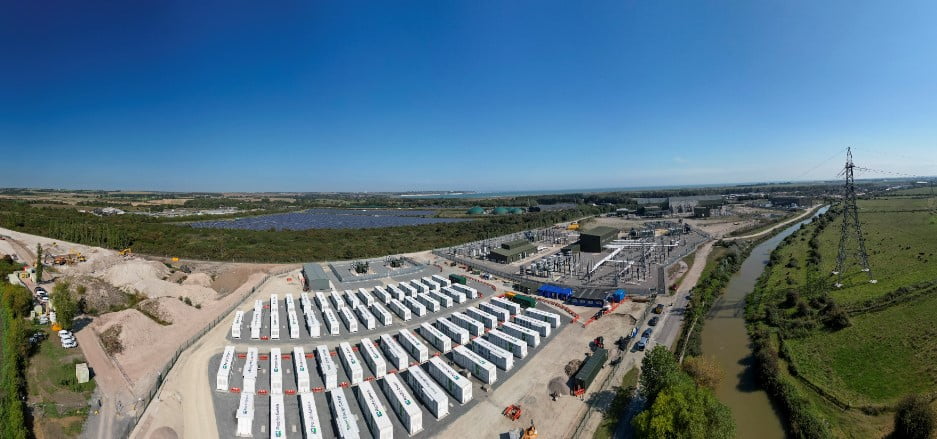
The company owns 50 Cactos One units (not specifying the split between Classic and Cardo) and with the latest financing said that can grow to over 1,000 in the coming years. The investment period is expected to be 2.5 years with an operational period for the units of 10 years.
Its largest owned system is a 2.5 MWh BESS installed at a logistics centre in Tuusula, Finland.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 9th annual Energy Storage Summit EU in London, 20-21 February 2024. This year it is moving to a larger venue, bringing together Europe’s leading investors, policymakers, developers, utilities, energy buyers and service providers all in one place. Visit the official site for more info.
Continue reading