Had it dropped any further, the results could have been serious, with blackouts and other disruptions to supply as well as potential damage to infrastructure. While it isn’t yet clear exactly what happened in the chain of events, it was precipitated by a loss of 1GW of load from the IFA Interconnector between the UK and France.
It came during a couple of days of high renewable generation, with a record-breaking 21GW of wind on the system the previous day, there was around 19GW of wind – well over 50% of the 30GW to 35GW of total generation on the Great Britain (GB – the UK would include Northern Ireland, which shares its grid with the Republic of Ireland) grid.
The interconnector trip therefore took about 3% of total power off the network in one go.
“This is a reality of the new interconnected grid that we’re operating. With traditional power stations, big loads do not tend to drop off instantaneously, whereas interconnectors do. A big generator will wind down very slowly unless there’s a catastrophic event, but the interconnectors quite often seem to trip very large loads off of the system,” Hollies told Energy-Storage.news.
“So you’ve got this situation where you’ve got high renewables and then a good really big chunk of the system got lost instantaneously.”
The UK has two arms to its electricity network operation. One is National Grid, which is the transmission system operator (TSO), physically operating and managing the grid infrastructure, while the other is National Grid Electricity System Operator (National Grid ESO), managing and coordinating supply of electricity in real-time.
In that context, it’s the ESO that offers markets for grid-balancing services like frequency response and it is currently reforming the balancing reserve products available. The rollout of its dynamic frequency services as part of this, includes Dynamic Containment, the ancillary service which Hollies said is the post-fault service, and “the thing that’s supposed to really catch these big incidents, when there’s a huge, quick frequency deviation”.
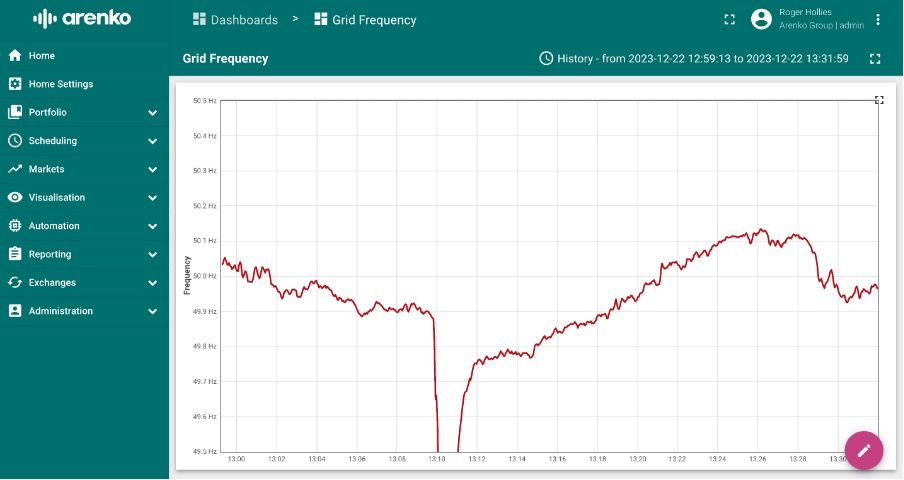
“And it looked like it worked. In the first instance, the 1GW dropped off, you saw the initial frequency response dropped to about 49.5Hz. But then something else happened we had this really deep, deep dip to 49.2Hz.”
The fact that disaster was averted and the frequency was kept within the boundary of 49.2Hz means that the safeguards in place ultimately worked. A serious blackout event did happen in 2019 after a frequency drop to 49.55Hz that happened in fewer seconds than was the case this time. It’s a good news story in that respect but Roger Hollies said it was, “really, really close, probably a lot closer than they were expecting,” in the ESO control room.
Roger Hollies posted this screenshot from the day of Arenko’s Nimbus platform to LinkedIn, joking that “the grid broke my graph!” given that the frequency dropped to a value no longer typically included in the axis. Image: Roger Hollies via LinkedIn.
‘Batteries do it cheaper, and better’
The GB grid experiences high levels of volatility in its frequency, due to the high penetration of renewables and its islanded situation.
Battery storage has been able to compete widely in its ancillary services markets since 2016, when National Grid (prior to a split into two separate entities with the ESO) launched a world-first competitive tender for 200MW of enhanced frequency response (EFR).
Since then, the UK has raced into a leading position for battery storage deployment ahead of its continental European neighbours and an installed base of more than 4GW of large-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) assets.
Arenko’s Roger Hollies said in a post to LinkedIn prior to our conversation that due to the reduced value of frequency response markets, only about 80MW, or a third, of a portfolio of assets the company manages on its Nimbus software platform was contracted to deliver the grid services needed.
More importantly perhaps, Hollies noted that the post fault correction which was dispatched through the Balancing Mechanism – through which the ESO matches supply and demand in real-time – featured little to no instructions for batteries to step in.
In other words, there has been enormous investment into BESS in the UK (including Northern Ireland) since 2016 and much of that has directed resources into providing frequency regulation.
While that investment enables batteries to participate in maintaining the frequency day-to-day, much less regard has been paid to what batteries can do during more critical events and in post-fault correction such as following what happened at lunchtime on 22 December.
Roger Hollies said the UK is leading on a lot of energy transition issues, and he acknowledged that the ESO has a difficult job to do and is taking steps in the right direction, such as the recent launch of the Open Balancing Platform for dispatching the Balancing Mechanism and other services.
Indeed, National Grid ESO is doing “really good work”, according to the Arenko CTO, faced with the intertwined duties of keeping the electricity grid online and reforming the grid’s balancing services simultaneously.
However the ESO needs to communicate their problems to the industry, and the industry to apply its “incredible minds, incredible resources” to figuring out the wider role or roles that BESS can play in keeping the lights on.
‘Gas’ contribution to reserve will erode this year’
Batteries are gradually coming in and replacing the grid’s traditional support systems, and Hollies points to various studies that show they can do so considerably more cheaply than those legacy technologies. That’s already been seen with frequency response: eight years ago, there were no batteries providing frequency services to the GB grid, now they dominate. The groundwork now needs to be done for that to extend into reserve and other services, Hollies argued.
“There’s a really positive message of batteries coming in replacing traditional generation fossil fuel generation,” he said, noting that he and Arenko recently attended COP28, where his main conclusion was that “fossil fuel companies are not going to move quickly enough [on climate], because they just won’t”.
“It’s their business. So what we have to do as an alternative industry is to replace and provide the services that they provide, better and cheaper. We’re seeing that with frequency response, that’s been done, batteries now dominate the market.
“Reserve is a huge volume of market and I think we’re going to slowly see this year particularly, batteries are just going to erode gas’ contribution to reserve massively and that’ll hopefully trigger another another investment push into batteries in the UK.”
An open transparency forum is being held on the interconnector trip and subsequent frequency event today (Wednesday 10 January), which Hollies said hopefully would shed some light and give the industry food for thought in how it could put its ideas forward.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 9th annual Energy Storage Summit EU in London, 20-21 February 2024. This year it is moving to a larger venue, bringing together Europe’s leading investors, policymakers, developers, utilities, energy buyers and service providers all in one place. Visit the official site for more info.
Continue reading