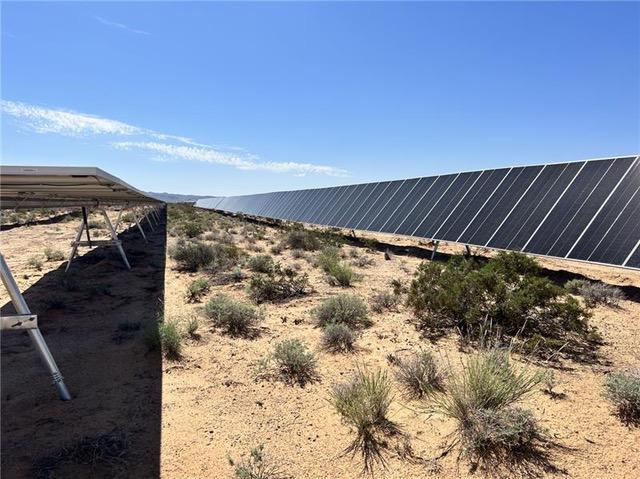
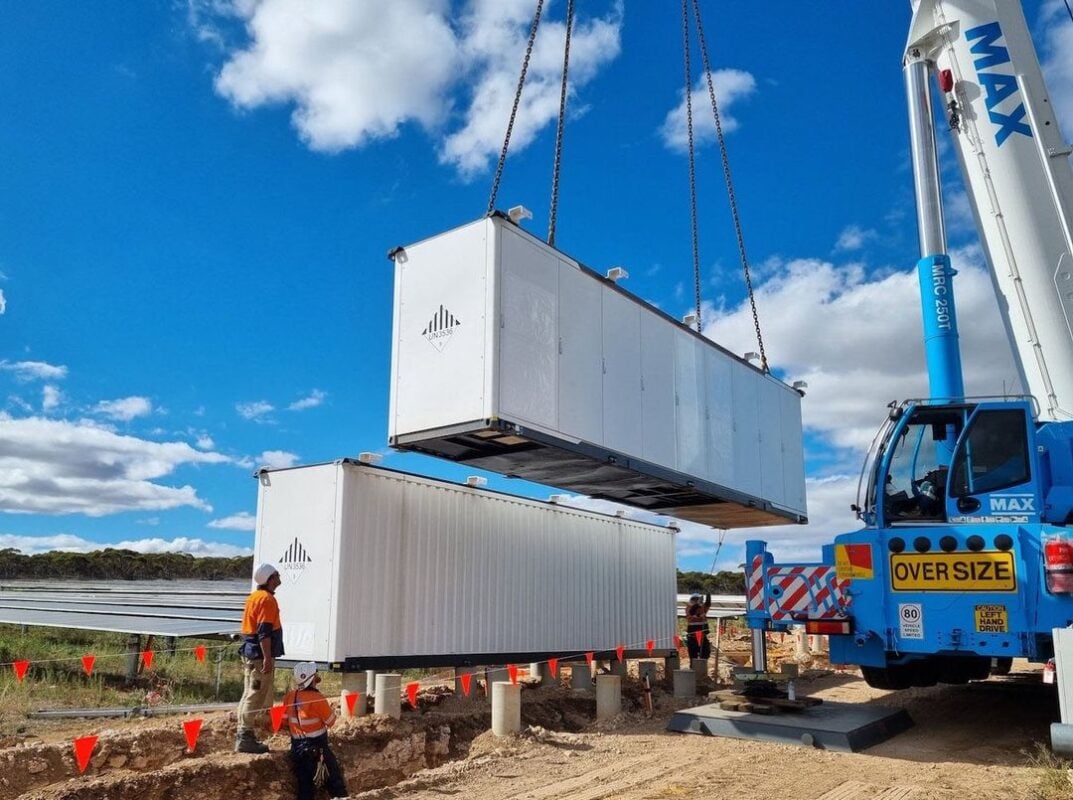
Solar panels on public lands in Nevada. (Photo Credit: BLM Southern Nevada District Office)
The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) has announced its proposed roadmap for solar energy development on public lands across the West.
The BLM hopes the release of the Final Utility-Scale Solar Energy Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement and Proposed Resource Management Plan Amendments (also known as the proposed updated Western Solar Plan) will support continued progress on responsible permitting.
The plan would make 31 million acres of public lands across 11 western states available for potential solar development, driving development closer to transmission lines or on previously disturbed lands and avoiding protected lands, sensitive cultural resources and important wildlife habitat.
Steering project proposals away from areas where they may conflict with other resources or uses is expected to help ensure responsible development and speed up the permitting process.
The plan updates and expands the original 2012 Western Solar Plan in order to reflect changes in technology and meet the higher demand for solar energy development. This plan analyzes Idaho, Montana, Oregon, Washington and Wyoming, in addition to the six states analyzed in the original plan.
“The updated Western Solar Plan is a responsible, pragmatic strategy for developing solar energy on our nation’s public lands that supports national clean energy goals and long-term national energy security,” says BLM Director Tracy Stone-Manning.
“It will drive responsible solar development to locations with fewer potential conflicts while helping the nation transition to a clean energy economy, furthering the BLM’s mission to sustain the health, diversity and productivity of public lands for the use and enjoyment of present and future generations.”
No solar developments are authorized through this planning effort. Proposed projects will still undergo site-specific environmental review and public comment. This Final Utility-Scale Solar Energy Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement follows a draft published in January for public comment.
In total, BLM has now permitted clean energy projects on public lands with a total capacity of 29 GW.
Continue reading