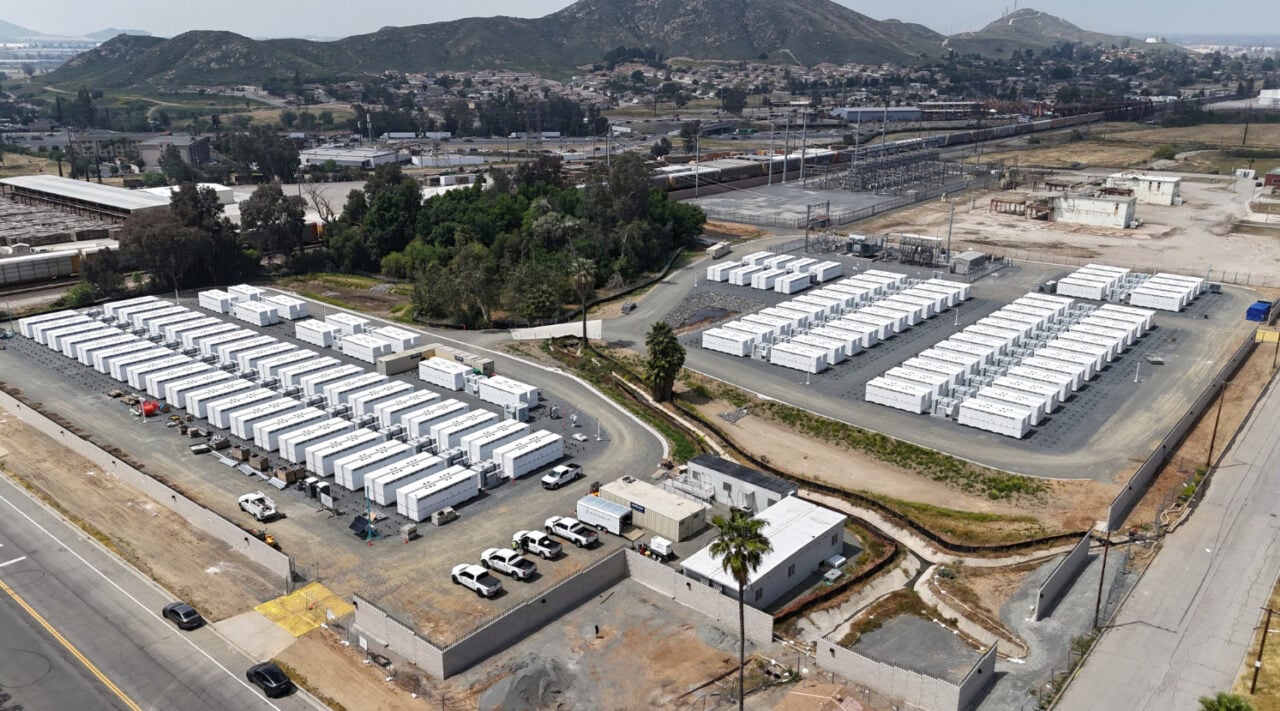
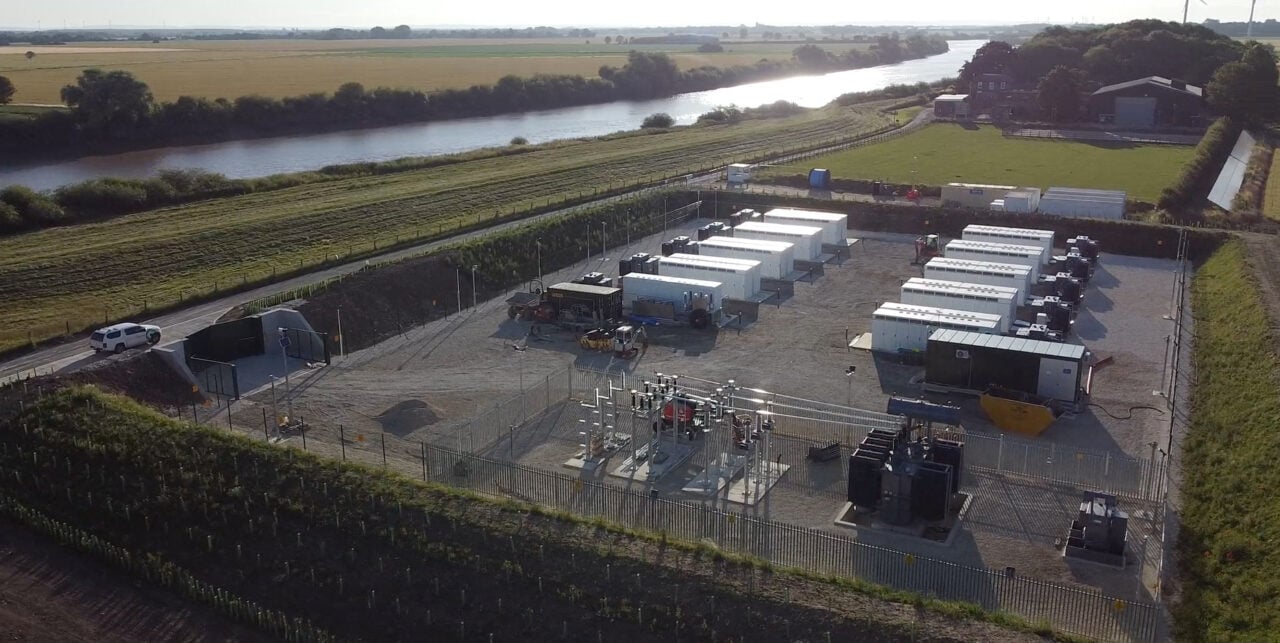
Arevon secured financing to complete the project earlier this year, with a US$350 million of preferred equity and debt financing with Blackstone Credit & Insurance, as reported by Energy-Storage.news.
California is the leading state in the US for BESS with around 9GW online by July 2024 according to transmission system operator (TSO) CAISO with high renewable penetration and ambitious decarbonisation targets.
Arevon, a developer and independent power producer (IPP), is among the most active in the US solar and storage markets. Recently, it secured a deal for the offtake of its 1GWh Cormorant BESS in California with community choice aggregator (CCA) MCE shortly before securing financing for a solar-plus-storage project with a 600MWh BESS.
“The Condor Energy Storage Project signifies our ongoing commitment to energy storage technologies and to advancing clean, renewable energy across the nation,” said Kevin Smith, Arevon CEO.
“As California looks to achieve its sustainability goals and brings more renewable energy online, battery storage is an essential component to ensure grid reliability and facilitate further renewable energy adoption. Our projects here provide viable economic revenue, cleaner air for the community, and reliable energy access throughout the state.”
EMS: Wärtsilä’s new GEMS 7 platform, Generac buys microgrid controls specialist
While the monitoring, controls and optimisation platform can serve as an energy management system (EMS) for all manner of energy assets including thermal, renewable energy storage at portfolio, fleet and single asset level, it has its strongest market presence in battery storage.
GEMS 7’s design features partly reflect the growing average size of customer projects in the grid-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) space, the company claimed.
GEMS Digital Energy Platform—to give the EMS its full monicker—can support equipment from a wide variety of power electronics and battery storage manufacturers. That includes Wärtsilä’s own GridSolv Quantum range of containerised battery storage, the newest iteration of which was launched in March this year.
The platform uses machine learning techniques alongside historic and real-time data analytics to optimise energy assets and balance portfolios.
Its digital capabilities were among the chief reasons why Wärtsilä acquired GEMS’ creator, Silicon Valley-based BESS integrator Greensmith Energy in 2017, using the acquisition to kick off the Finnish marine and energy solutions provider’s energy storage business.
The company said this morning that in response to customer requirements, GEMS 7 is designed to be able to control multi-gigawatt-hour scale BESS plants with fast response times, and at the same time offer visibility into storage assets down to the battery cell level.
Other changes include the addition of new visualisation interfaces for the management of large sites, the ability to ‘partition’ sites down to allocate different revenue-generating applications and controls to enable cell balancing and state of charge (SoC) calibration.
It also has new alarm and remote monitoring management features, module-level data access, and reduced latency for responding to grid frequency events.
“An effective software system meets increasingly short response time requirements, provides ample data for monitoring and analysis to remote asset management teams, and is adaptable to changing grid requirements like synthetic inertia,” Wärtsilä Energy general manager for software product management Ruchira Shah said.
In a 2022 interview with Energy-Storage.news, Wärtsilä ES&O head Andy Tang commented on the ongoing increase in average customer project sizes, which at the time stood at around 100MW/200MWh, Tang claimed, a trend which appears to have continued since.
Generac buys out microgrid controls and EMS provider
New York Stock Exchange-listed backup power generation product manufacturer Generac has acquired Colorado-headquartered microgrid EMS specialist Ageto.
The company announced yesterday (5 August) that the deal to take over Ageto closed at the beginning of the month.
Ageto makes microgrid controllers for systems that combine and integrate different distributed energy resources (DERs), including energy storage and solar PV, as well as other power equipment from conventional generation to electric vehicle (EV) charging.
Ageto microgrid controllers have been incorporated into Generac battery storage system solutions and gensets since 2021, like Wärtsilä’s GEMS suite enabling the control, monitoring and optimisation of assets via a single interface. Its products are primarily aimed at the commercial and industrial (C&I) market.
Generac is best known as a manufacturer of standby generators for home and C&I use, but with business lines in everything from portable power solutions to EV chargers and even pressure washers.
The company entered the battery storage business following the 2019 acquisition of home storage system and inverter manufacturer Pika, subsequently launching its own brand home battery solutions, and forming Generac Grid Services post-takeover of distributed energy tech platform provider Enbala.
The C&I energy storage space has typically been the slowest moving of the three major market segments alongside residential and utility-scale. Research firm Wood Mackenzie found that in Q1 2024, 993MW/2,952MWh of new utility-scale storage was deployed in the US, alongside 252.4MW/515.7MWh of residential installs, but just 19.4MW/44.4MWh of C&I and community-scale storage was deployed in the quarter.
However, fundamental market drivers mean the C&I segment holds strong potential over a 10-year outlook, Wood Mackenzie said in its Q1 2024 US Energy Storage Monitor report.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 1st Battery Asset Management Summit USA in San Diego on 12-13 November 2024. Featuring a packed programme of panels, presentations and fireside chats from industry leaders focusing on Connecting Asset Owners and Optimizers to Maximize Strategies for Storage Assets. View the website today
US Bureau of Land Management progresses 6.2GW of BESS at hybrid PV projects in Nevada and Arizona
At final buildout, the nine projects have the potential to house 6.2GW of BESS capacity with up to 7.17GW of co-located solar across 124,500 acres of public land managed by the BLM.
Esmeralda 7 Solar – 5.2GW of BESS capacity
Central to the recent announcement is the issuance of a Draft Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) and Resource Management Plan Amendment for a group of seven hybrid solar and BESS facilities located in Esmeralda County, Nevada, known collectively as the Esmeralda 7 Solar development, which is now subject to a 45-day public comment period.
Publication of this document is an important first step for the Bureau of Land Management which will use it, along with any comments received, to conduct individual environmental analysis for each of the seven projects. The BLM will then use this information to decide whether or not to grant each development a right-of-way (ROW) authorisation, allowing for the construction and operation of the hybrid facilities.
Details of the Esmeralda projects currently under BLM review can be found in the table below:
Project nameDeveloperProject SubsidiaryBESS output (MW)Solar PV capacity (MW)Acreage Lone Mountain SolarLeeward Renewable EnergyUS Solar Assets, LLC5001,0008,350Nivloc SolarInvenergyNivloc Solar Energy, LLC5005008,280Smokey Valley SolarConnectGen CG Western Renewables III, LLC1,0001,0004,890Red Ridge 1 SolarAvantus335ES 8me, LLC6006006,190Red Ridge 2 SolarAvantus335ES 8me, LLC6006006,860Esmerelda Energy CenterNextEra Energy ResourcesBoulevard Associates, LLC1,0001,0008,360Gold Dust SolarArevia PowerGold Dust Solar, LLC1,0001,50016,720A summary of the seven projects currently under BLM review. Information is based on preliminary plans and is subject to change. Source: US BLM.
Each project is expected to connect to the local electricity grid through NV Energy’s Esmeralda substation, via the utility’s Greenlink West 525 kV transmission line that has yet to be built.
Construction on each project is expected to take 18-36 months, and the full buildout of all projects is expected to be complete within five years of receiving BLM approval.
700MW of lithium iron phosphate battery storage
In the last month, the BLM has also published a final EIS for Leeward Renewable Energy’s Libra Solar facility which is set to comprise a 700MW BESS co-located with a 700MW solar farm located across 5,100 acres of land in Mineral and Lyon Counties, Nevada.
The BLM will decide whether to grant a ROW for Leeward’s Libra development after the document’s 30-day availability period ends on August 26 2024.
Leeward is expected to utilise 3.7-hour duration lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery packs for its Libra project, although the developer has stated it will use the “best technology” available at the time of construction. Leeward is expected to break ground on the project at the end of this year.
Arevia Power’s Elisabeth project
Arevia Power has also witnessed progress with another one of its projects, after the BLM issued a draft environmental assessment (EA) for the developer’s Elisabeth Solar facility located in Yuma County, Arizona.
The Bureau of Land Management is holding a virtual public meeting on 14 August 2024 to discuss the EA, and expects to make a decision on whether to grant the developer a ROW authorization in November this year.
It’s anticipated that Arevia Power will utilise lithium-ion technology for the 300MW BESS at the Elisabeth facility that will be co-located with a 270MWac solar farm.
Region home to ‘US’ largest co-located, single phase solar-plus-storage project’
The southwestern portion of the US is home to some of the country’s largest renewable developments, with this recent announcement from the BLM showing that this isn’t set to change anytime soon.
Quinbrook Infrastructure Partners and Primergy Energy recently announced that its Gemini solar-plus-storage project in Nevada had been brought online, covered in Energy-Storage.News during July.
A spokesperson from the companies told Energy-Storage.News that the development is the “largest co-located, single phase solar plus storage project” operating in the US.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 1st Battery Asset Management Summit USA in San Diego on 12-13 November 2024. Featuring a packed programme of panels, presentations and fireside chats from industry leaders focusing on Connecting Asset Owners and Optimizers to Maximize Strategies for Storage Assets. Energy-Storage.news Premium subscribers can benefit from exclusive discounts on tickets. View the website today
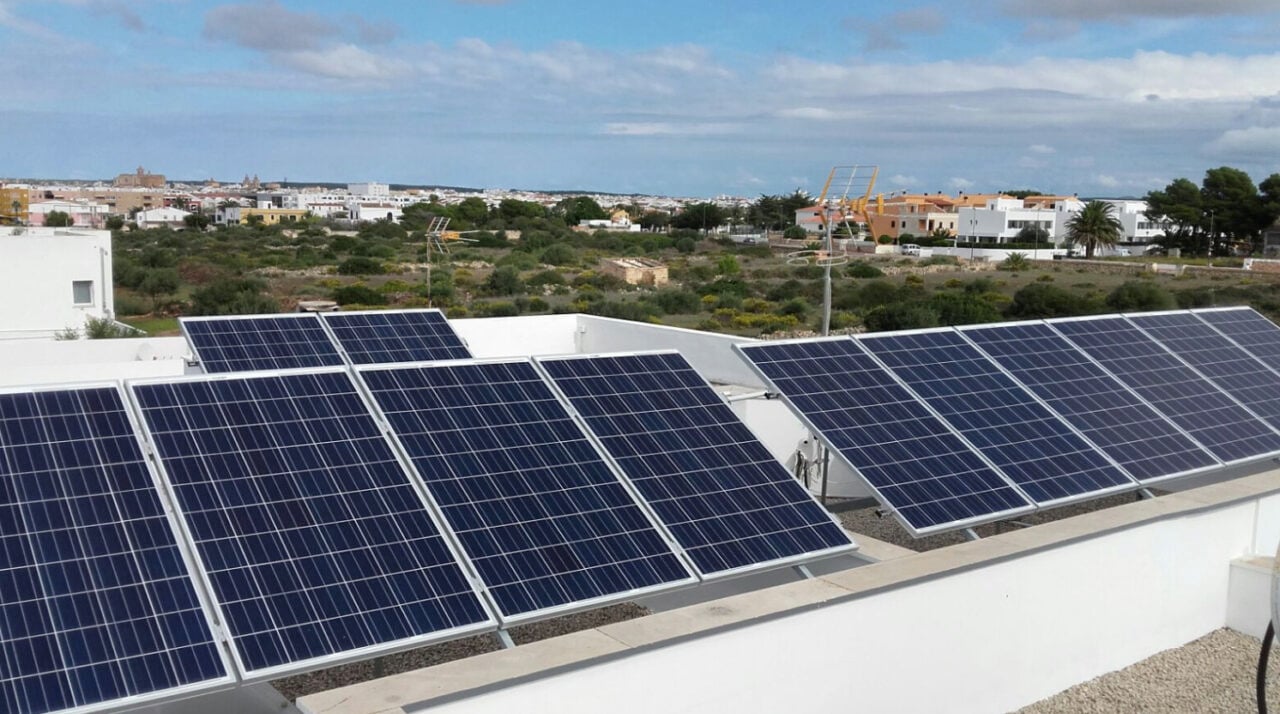
Spanish island Menorca investing in 18MWh of distributed battery storage
It will invest in 9.24MWp of solar PV across pergolas in car parks and roofs of public buildings for self-consumption and creating ‘local energy communities’, adding to 4.5MWp that is already operational.
Along with this it will add BESS, a technology which is less developed on the island currently, the Council said. The 18MWh to be deployed will be linked with the publicly owned generation and self-consumption facilities, in operation or planned.
See how the capacity additions split out by municipality in the table below.
MunicipalityPV (MWp)Batteries (MWh)Alaior0.640.7Ciutadella0.910.94Es Castell2.988.46Es Mercadal0.610.49Es Migjorn0.360.44Ferreries1.835.23Mao1.10.93Sant Lluis0.830.81Total9.2618Source of data: Consell Insular de Menorca.
For more information about the investment plans and details about the PV and EV charging installations, see the Council’s announcement (in Spanish) here.
On mainland Spain, the grid-scale energy storage market is expected to boom in the next few years largely driven by government tenders, covered here and here, as well as the emerging business case of energy storage smoothing out solar generation.
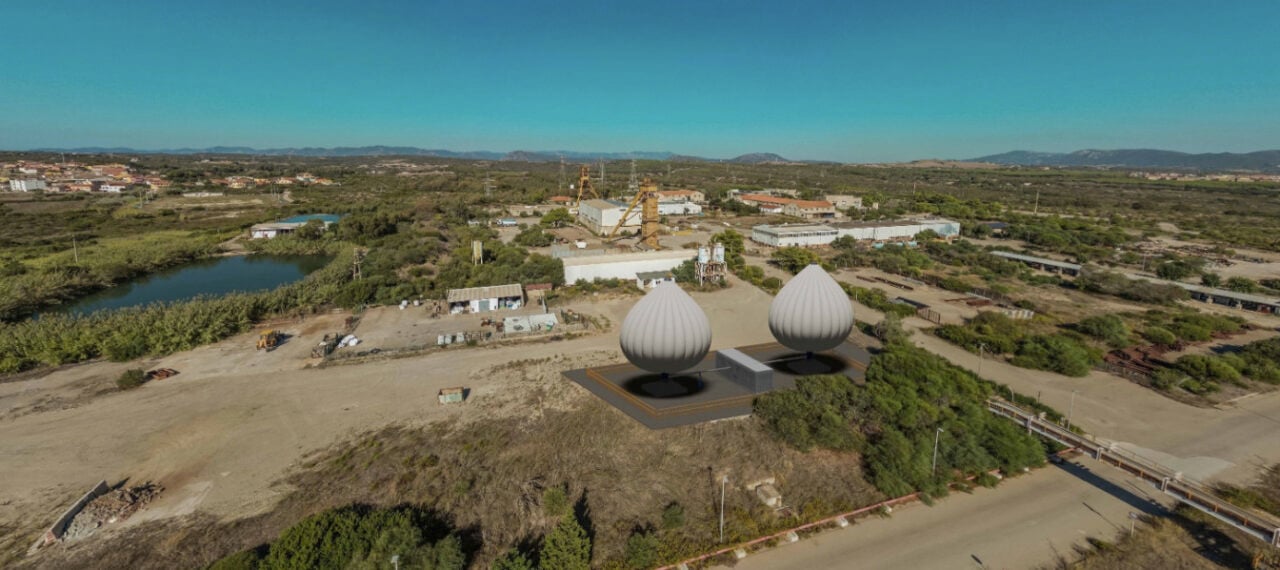
Energy Vault and municipality developing gravity-plus-BESS project at coal mine in Italy
It combines its proprietary gravity energy storage technology for which it is known and battery energy storage system (BESS) technology, and would be deployed in a large coal mine shaft that Carbosulcis is set to fully retire in 2026, called Nuraxi Figus.
Carbosulcis is owned by the Autonomous Region of Sardinia, the large Mediterranean island that is part of Italy. The Sardinia government wants to turn the coal mine into a Carbon Free Technology Hub to aid the industrial and economic development of an area heavily affected by the phase-out of coal production.
The solution would comprise a form factor of Energy Vault’s gravity tech that also combines with a water-based, modular pumped hydro application, though the company didn’t say more about how this would work. It would also utilise the company’s VaultO energy management software (EMS).
Installation of the first modular gravity components will begin in September 2024 with the testing of the underground component of the Hybrid Energy Storage System expected to be completed in 2025.
Energy Vault revealed a number of new form factors of its gravity storage tech earlier this year, including one for use in skyscrapers in partnership with world-leading architecture consultancy SOM.
The company has had several projects commissioned recently, including a BESS in Texas and its first gravity storage project in China, and will release its financial results for the most recent quarter after markets close today.
VIDEO: From Cell to Complete AC System Integration with Trina Storage Elementa 2
Additionally, the complexities and competitiveness of applications, merchant markets, and contracted opportunities are higher than ever before.
In this session, we explore Trina Storage’s latest innovation, the Elementa 2 Battery Energy Storage System. As one of the few integrators with the capability to manufacture battery cells and provide fully integrated AC turnkey systems, the company’s unique vertical integration process comes under the spotlight.
We delve into the market trends driving the need for advanced BESS solutions, the technical specifications and benefits of Elementa 2, and an overview of Trina’s state-of-the-art manufacturing and integration facilities.
Trina Storage is ranked as a Tier 1 energy storage provider by BloombergNEF, just three years after delivering its first Elementa project outside China, at Burwell in Cambridgeshire, England.
Energy storage technology is moving fast, and leading players in the industry, like Trina, are at the forefront of making those advances happen.
A presentation from Trina Storage head of battery storage engineering, Beyond Li, is followed by an interview-style discussion with Energy-Storage.news editor Andy Colthorpe. After that we have our usual audience Q&A session.
Speaker:
Beyond Li, head of BESS solution engineering, Trina Storage
[embedded content]
You can also register to watch the webinar from the on-demand section of the site, which will also enable you to access presentation slide deck, and where you can find all our other Energy-Storage.news webinars.
UK Roundup: 580MWh of projects from Harmony Energy, Envision, Field and Quinbrook
Developed by Harmony Energy, the project’s construction was managed by Tesla with oversight by the Harmony Energy project team. The battery energy storage system (BESS) will be located in Rusholme and is expected to be fully operational in all markets in early August.
Harmony Energy is a developer and investment advisor to the Harmony Energy Income Trust fund.
The BESS will operate through Tesla’s algorithmic trading platform, Autobidder, which has already been deployed at other Harmony projects.
To see the full, original version of this article go to Solar Power Portal.
Envision Energy to supply BESS for 50MWh Field project
Envision Energy has partnered with renewable energy infrastructure firm Field to develop a 50MWh battery energy storage system (BESS) in Blackburn, England.
Envision Energy will supply the Field Whitebirk project with the necessary hardware and equipment to install the BESS onsite. The agreement is part of a long-term partnership aimed at helping Envision’s energy storage division in the UK and Europe.
Mark Walton-Hayfield, senior director for energy storage in the UK and Ireland at Envision Energy, said: “We are proud that our advanced BESS solutions have been recognised by Field for their exceptional standards in safety, reliability and technical capability. We are excited to bring our Tier 1 technology to Whitebirk whilst continuing to collaborate and partner with Field more broadly and make a significant contribution to the global energy transition.”
To see the full, original version of this article go to Solar Power Portal.
Construction starts on E.ON and Quinbrook’s 460MWh BESS
Construction is underway on a new battery energy storage system (BESS) project, set to be one of the UK’s largest.
The project, located on the site of a former coal-fired power station in Uskmouth, South Wales, is a collaboration between major international energy firm E.ON and global investment manager Quinbrook Infrastructure Partners.
Building work is being undertaken by local firm Jones Bros Civil Engineering UK, which states that activity is currently focused on developing the foundations for the battery and the power conversion systems (PCS) units, as well as the primary and secondary substations and transformers.
Part of the development plan involves significant ecological enhancement, including the development of a new sustainable energy park and landscaping work to make the area more appealing to wildlife, including otters and water voles.
Construction is expected to be completed by the first quarter of 2025.
To see the full, original version of this article go to Solar Power Portal.
Planning permission for 23MW solar project with 57MW battery storage facility
The minister of state, Matthew Pennycook, has granted planning permission for a 23MW solar development with 57MW of battery storage to be installed in Warwickshire.
Set to be operational for 40 years, a revised application was submitted for the solar and storage project by Enso Green Holdings in October 2022. Enso Energy is a renewable energy developer that recently co-developed the first solar and storage project to be connected at a transmission level.
Pennycook, the minister who approved the plans on behalf of the secretary of state, has been vocal in his support of solar development in the UK.
The Warwickshire project, Honiley Road Solar Farm, had been approved by the Warwickshire District Council planning committee in July 2023 but was ‘called in’ by the then-secretary of state for the Department for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities in February this year.
To see the full, original version of this article go to Solar Power Portal.
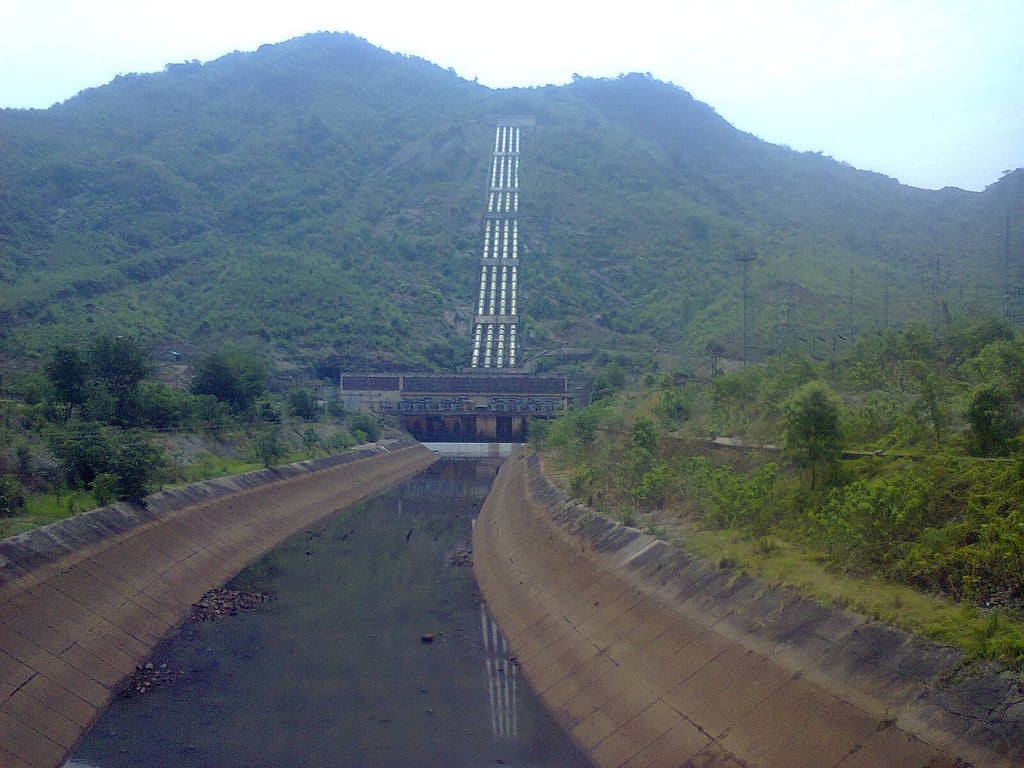
Government fast track towards construction for two pumped hydro projects in India
This, the authority said, is in order to enable their commissioning “on a fast track”. The announcement comes shortly after the government’s finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman pledged in the Union Budget 2024 that PHES plants would be supported by policy measures.
The CEA advises the Indian government on policy and formulates electricity system plans. As regular readers of Energy-Storage.news may have seen, its National Electricity Plan 2023 which helps guide the Ministry of Power called for large deployments of both battery energy storage system (BESS) and PHES-based energy storage in the coming years.
As India targets 500GW of new non-fossil fuel energy by 2030, and net zero emissions from all sectors of the economy by 2070, the integration of storage into the power system will become increasingly vital, the CEA and government have projected.
By the 2031-2032 timeframe, that equates to about 47GW/236GWh of grid-connected batteries, and 27GW/175GWh of pumped hydro, for a total 74GW energy storage output and 411GWh capacity.
By 2047, CEA modelled that a total of 320GW/2,380GWh will be needed, with 230GW/1,840GWh from battery storage and 90GW/540GWh from PHES.
176GW of pumped hydro potential across India
CEA said that it has so far received around 60GW of proposals for PHES projects, currently at the Survey & Investigation stage, ahead of detailed project reports (DRPs) being put together.
The two projects selected last week are the 600MW Upper Indravati PHES in Odisha, being developed by Odisha Hydro Power Corporation (OHPC), and the 2000MW Sharavathy project in Karnataka, in development through Karnataka Power Corporation Ltd (KPCL).
Upper Indravati would see pumped hydro capacity added to an existing 600MW (4 x 150MW unit) hydroelectric power plant. According to OHPC’s website, the corporation also wants to add pumped hydro to two other operational hydro plants, the 320MW Upper Kolab plant and 510MW Balimela plant.
Sharavathy meanwhile appears to be a 2,000MW PHES addition to an existing 1,035MW pumped hydro plant in Karnataka.
In addition to fast-tracking the two plants towards DRP status, the CEA has revised its guidelines for submitting projects into planning, which again is aimed at streamlining and speeding up the process.
CEA noted that in addition to the 60GW of submitted proposals, India currently has 4.7GW of PHES plants in operation, 4GW already under construction and 3.6GW have ‘concurred,’ meaning construction is to be started. India’s total PHES, or pumped storage plant (PSP) potential, to use CEA’s own terminology, is about 176GW, the authority said.
See more of Energy-Storage.news’ coverage of the energy storage sector in India, including recent tenders for standalone energy storage, renewables-plus-storage and Firm Dispatchable Renewable Energy FDRE.
Belize and US Virgin Islands progress large-scale BESS projects
The Ministry of Finance, Economic Development and Investment is seeking expressions of interest (EOI) from consultants and experts to assist it with the Belize Renewable Integration and Resilient Energy System Project, using World Bank funding.
Interested consultants have until 2pm local time on 8 August—this coming Thursday—to provide information demonstrating their suitability to provide goods, consulting and non-consulting services for the project.
Contact details for the EOI process can be found here.
The Belize Renewable Integration and Resilient Energy System Project is aimed at improving the resilience of the electricity system against extreme climates by strengthening the national transmission infrastructure.
It will fund the acquisition and deployment of BESS to enable the integration of renewable energy onto the grid, and improve resiliency and reliability of electrical supply. A total of US$65 million will be invested in the project, according to the World Bank.
The project’s primary implementing agency is Belize Electricity Limited, the country’s main utility and network operator.
It comes shortly after nearby Honduras progressed the reform of its electricity market to enable the deployment of energy storage at scale on its grid.
Wärtsilä completes generators-plus-BESS on US Virgin Islands
In concurrent news, the publicly-owned utility for the US Virgin Islands has announced the completion of a new BESS alongside upgrades to an existing gas power plant, the Randolph Harley Power Plant (RHPP).
The Virgin Islands Water and Power Authority (WAPA) announced the completion last month (24 July) after which it began final commissioning of the generators and BESS equipment.
As Energy-Storage.news reported when the project neared completion last year, system integrator Wärtsilä provided a hybrid solution combining four 9MW fossil fuel engines together with a 9MW, 2-hour duration (18MWh) BESS unit. The company got the contract for the job in 2020, which was delayed due to Covid-19.
The fossil fuel engines totalling 32MW of power run on liquid petroleum gas (LPG) and light fuel oil (LFO).
Finland-headquartered Wärtsilä is active in supplying island power solutions, also providing a 25MW/25MWh BESS on another Carribean island, Curaçao.
Earlier this year, the Comisión Nacional De Energia of the Dominican Republic started construction on a 99MWh BESS in the country.
Eku Energy finances battery storage project in Japan with ‘first-of-a-kind’ tolling deal
“There are certain major milestones to hit until a utility scale battery energy storage system is ready to support the grid and be a major contributor to the #energytransition. Financial close is certainly one of those,” the developer posted.
As reported by Energy-Storage.news in April, the company’s Hirohara BESS project will be a 30MW/120MWh (4-hour duration) asset in Oazu Hirohara, a region of Miyazaki Prefecture on the southern Japanese island of Kyushu.
It appears this site jumped the gun a little in reporting that previous announcement, assuming that financial close had already been achieved at that time, but as the post on Friday clarified, that is now the case.
Eku Energy said the financial close is a ‘major milestone’ in preparing a BESS project to contribute to balancing the grid, and that the latest development showed the developer is ‘on track to hit all future milestones as planned’.
Offtake deal with Tokyo Gas
Perhaps most notable about the project is the claimed “first-of-a-kind” offtake deal within the Japanese market that Eku Energy has signed for it, with utility company Tokyo Gas.
Tokyo Gas has contracted for full operating rights over a 20-year term to the Hirohara BESS, which Eku Energy will own. In April, the utility said in a Japanese-language press release that the project marked its first steps towards full-scale entry into the grid battery storage business.
Tokyo Gas would use its experience in energy trading markets to use battery storage to contribute to stabilising the grid and enabling greater integration of renewable energy.
At the same time, Tokyo Gas will also leverage the control capabilities of behind-the-meter (BTM) battery storage systems installed at customer premises, which could include commercial and industrial (C&I) facilities.
It is also a first in Japan—although not a first BESS project internationally—that Japanese bank MUFG has participated in project financing for. The bank is becoming somewhat prolific in the sector, particularly in the US, where last week Energy-Storage.news reported its involvement in a US$515 million finance raise by developer Eolian, and US$258 million secured by esVolta.
Eku Energy also said in its LinkedIn announcement that construction partners on the Hirohara BESS include integrated systems engineers Kinden Corporation, renewables specialist Looop and Fortec Architects, all Japan-headquartered companies.
‘Multiple commercialisation pathways’ for BESS in Japan
At the Energy Storage Summit Asia 2024, held last month in Singapore and hosted by our publisher Solar Media, Eku Energy’s APAC technical lead Nick Morley said that having started his career in clean energy working at a solar panel testing facility in Yokohama, Japan, he was “very excited to be working on a BESS project in Japan now”.
Eku Energy has only been around in its present form for about a year-and-a-half and has projects under construction or in development in Australia, the UK and Italy.
Japan’s BESS market is in its relative infancy, and a lot of interest has been created recently by the Long Term Decarbonization Auction (LTDA), a new capacity market opportunity through which batteries and pumped hydro energy storage (PHES) projects were awarded a combined 1.67GW of 20-year contracts.
However, speaking in a panel discussion on Japan at the Asia Summit, Eku’s Nick Morley said that developer “knows for sure that the LTDA is not the only way to commercialise projects in Japan”.
Morley said Eku believed its Tokyo Gas deal to be the first of its kind in the market.
“One of the things that’s attractive about Japan is that there are multiple commercialisation pathways there. It’s not completely dependent on the LTDA,” Morley said.
Yet, it is still early days for many of those pathways and Morley added that mechanisms like the LTDA coming from the policy space, as well as those “multiple commercialisation pathways” would both be beneficial in making Japan an attractive market for investment.
Fellow panellist Ross Bennett of German state-owned bank NORD/LB said that the LTDA is not the only way to finance a project or “the only way to obtain debt finance on a project” in Japan.
“We are also seeing other markets in long-term corporate offtake solutions. In Japan, there are several very large and strong credit-worthy players,” Bennett said.
Meanwhile, Bennett said, different types of contracts and financing which could include different blends of long-term contracts either with corporate offtakers or underwritten by government schemes, along with merchant revenues, will likely take some time to evolve in Japan, as has been seen in other markets. Once that takes off, it could happen quite quickly Bennett said.
Morley said that if the diversity of commercialisation strategies in the country increases, lenders can also become more comfortable with a degree of merchant risk exposure.
For Eku Energy, and perhaps others, like Pacifico Energy, which delivered Japan’s first two BESS projects trading in the wholesale power market, there could be an advantage in being early in entering the market.
“There is a kind of incentive for greater risk-taking behaviour from developers in the storage business. In many markets, time and again, we see that there is a major first-mover advantage,” Morley said.
Energy-Storage.news Premium subscribers can read the write-up of the Japan panel discussion from the Energy Storage Summit Asia 2024. For more information on next year’s Asia event, see the official website: ESN Premium subscribers can enjoy special discounts on tickets.