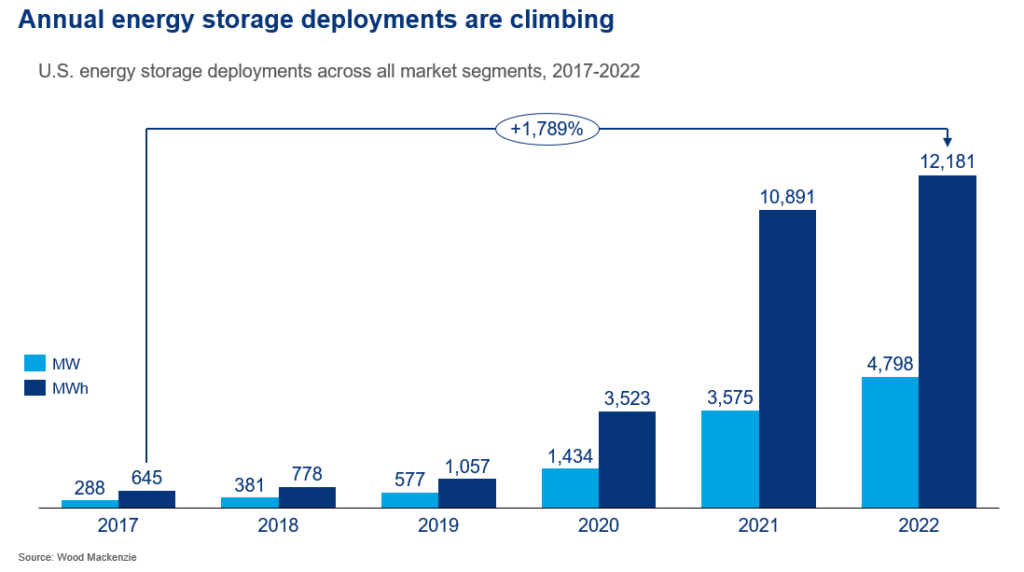
Microvast’s Energy Tech and Testing Center in Colorado. Image: Microvast.
Microvast, a technology innovator that designs, develops, and manufactures lithium-ion battery solutions, recently launched its new Energy Division with the anticipated release of an industry-leading battery energy storage system (ESS).
Microvast’s ESS offers 4.3MWh usable energy density per 20-foot container, one of the highest levels of energy density available on the market.
Additionally, Microvast’s ESS solution has superior energy retention and roundtrip efficiency capabilities.
“We are excited to launch the new Microvast Energy Division supporting the rapidly growing energy storage market, with an initial focus in the United States,” said Zach Ward, President of Microvast Energy.
“Our new energy storage system provides our customers with superior energy retention and roundtrip efficiencies, translating to significant economic advantages over competitive products.”
New Energy Division headed by industry veteran
Microvast is pleased to have Ward join as the head of the new Energy Division. Ward is an industry veteran with more than 18 years of experience in the solar energy sector as a senior executive for several of the largest and most active companies in renewable energy. He has executed more than 20GW of utility and distributed generation solar and 2GWh of energy storage projects.
Overseeing the Energy Division’s strategic initiatives, direction, operations, product development, sales, and key relationships, Ward has been actively recruiting and hiring a dedicated team composed of experienced industry personnel for the premiere of the new Energy Division and rollout of Microvast’s groundbreaking ESS container.
Speaking on the division’s new ESS solutions, Ward states, “Our utility-scale ESS container provides critical infrastructure capable of addressing the gap between renewable energy supply and peak grid demand. With the recent passing of the Inflation Reduction Act and the construction of our new 780,000 sq. ft. Tennessee manufacturing facility, we look forward to advancing clean and renewable energy initiatives.”
ESS container delivering industry-leading energy density
Microvast Energy Division’s priority is bringing its battery energy storage system, the ME-4300-UL ESS Container (the “ESS Container”), to the US market.
The ESS Container is designed for energy-shifting applications such as renewables integration, peak demand, and capacity support. The Microvast energy storage system delivers an industry-leading usable energy density of 4.3MWh per 20-foot container. This higher density equals fewer containers, a smaller footprint, easier installation, and less maintenance for utility-scale plants.
Additionally, the ESS Container offers a long battery life of more than 10,000 cycles under normal operating conditions, as well as easy transportation and installation for fast deployment at utility-scale plants, increasing overall project velocity.
Demonstrating Microvast’s commitment to becoming the leading provider of energy storage for utility-scale projects, the ESS Container is packed with features including:
The 6th generation battery management system (BMS) is developed and programmed in the United States to help ensure grid security
Ready-to-install, 20-foot liquid-cooled battery container with an industry-leading energy density of 4.3MWh per container (up to 30% more energy density than leading ESS containers)
Vigorously tested and qualified battery cells and modules based on Microvast’s proven commercial electric vehicle (EV) battery technology
Innovative safety features including fire suppression and explosion prevention systems
Expected to qualify as “domestic content” under the Inflation Reduction Act
“The superior performance of our products, domestic production capabilities, and our team’s ability to effectively execute large-scale utility projects sets Microvast apart. We believe our ESS solutions offer substantial benefits to our customers, including a lower total cost of ownership and expected eligibility for Inflation Reduction Act benefits,” Ward says.
Microvast’s ESS container will incorporate battery cells and modules manufactured in Clarksville, Tennessee. The Clarksville facility features 780,000 sq. ft. of manufacturing space on 85 acres and is expected to create hundreds of new jobs in the region.
“The Clarksville plant should contribute to the resilience of the domestic lithium-ion battery supply chain, create manufacturing jobs, and expand American battery capacity for the US power grid,” says Shane Smith, Microvast’s Chief Operating Officer.
New Energy Division adds depth to Microvast’s lithium-ion battery product portfolio
Although new to the stationary energy segment, Microvast is an established brand in the electric vehicle battery market, with more than 30,000 commercial and specialty vehicles in operation worldwide and over 17 years of experience in the design, development, and manufacturing of lithium-ion battery solutions.
The battery cell and module technology used for the ESS Container is built on the proven performance of Microvast’s lithium-ion battery solutions developed for the commercial electric vehicle (EV) market. The battery cells incorporate Microvast’s 53.5Ah NMC cell technology, boasting 235 Wh/kg of energy density.
“Energy customers can trust and depend on Microvast’s 17 years of proven expertise in lithium-ion battery manufacturing and our experience with 30,000 battery systems operational worldwide,” states Ward.
Cutting the ribbon to open the Colorado center. Image: Microvast.
Microvast’s new ESS solutions have been developed for grid-scale energy storage projects using the same proven technology as Microvast’s EV batteries, which offer very high energy density, outstanding safety features, and unmatched performance. Production of the ESS Container begins in 2023, with first customer deliveries happening in the second half of 2023.
“The positive response we have received from potential customers in the United States speaks volumes. Our future plans include expanding the ESS platform globally, leveraging our existing manufacturing facilities in Asia and Europe. We expect the current electrification trends to further accelerate and keep us very busy,” says Ward.
Microvast Energy wins big contract
Microvast Energy recently announced the securing of a large contract to supply a utility-scale battery energy storage system to a US customer. The energy storage portion of the project is 1.2GWh and will be co-located with a solar plant. The energy storage containers will begin shipping in 2023, with commercial operation expected in 2024.
“This project will help position Microvast as a leader in the utility-scale energy storage market while reducing carbon emissions and assisting the local utility in meeting its growing electricity needs,” explains Ward. “We’re excited to be selected as a key supplier for one of the largest energy storage projects in the United States.”
Continue reading