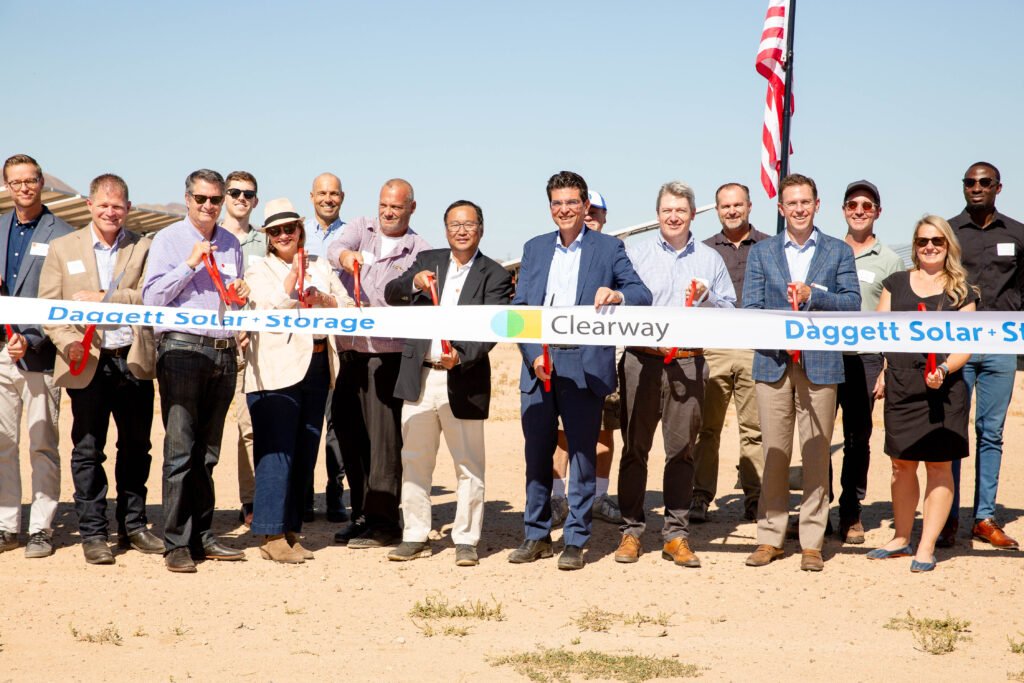
Clearway has also started construction on the two projects, a solar PV and a standalone battery energy storage system (BESS), located in the Californian counties of Fresno and San Bernadino.
The Solar PV plant in Fresno – the Luna Valley Solar Project – has a 200MW capacity, while the Dagget storage in San Bernadino has an output of 113.5MW. The storage project in San Bernadino is the final phase of a solar-plus-storage project with a PV capacity of 482MW and a storage output of 394MW.
Both projects are expected to reach commercial operations in 2025, while construction is carried out by renewables contractor Blattner Energy.
Moreover, the company has already secured a 15-year virtually paired hybrid power purchase agreement (PPA) with utility San Diego Gas & Electric for both projects. The remaining capacity of the Luna Valley PV plant is contracted under a 20-year PPA with utilities Southern California Edison and Power & Water Resources Pooling Authority.
“Luna Valley and Daggett 1 represent two major steps forward in California’s path to a reliable, affordable, and clean electric grid,” said Brooks Friedeman, VP of capital markets at Clearway.
In the past five years, the renewables developer has put over 2.3GW of solar and storage projects into construction and operation in California.
This story first appeared on PV Tech.
Japan: Expert panel discusses BESS market growth, opportunities and challenges
Speakers:
Shunsuke Kawashima, deputy general manager, Itochu Corporation
Ross Bennett, managing director and head of structured finance, NORD/LB
Joost van Acht, managing director, ib vogt
Dr Mahdi Behrangrad, head of ESS/VPP business development, Pacifico Energy
Nick Morely, APAC technical lead, Eku Energy
Drivers for energy storage in Japan
Itochu is one of Japan’s biggest wholesale trading companies (‘sogo sosha’). That means it is active in a wide range of business activities, including energy storage, where it has been a leader in residential battery sales.
It is now among the many Japanese and international players seeking to develop large-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) assets, and is partnered with the UK’s Gore Street Capital to manage a fund promoting storage and renewable energy in collaboration with the Tokyo Metropolitan Government.
Shunsuke Kawashima, who works across Itochu’s BESS business at all scales including residential, commercial and industrial (C&I) and utility-scale, opened the discussion by highlighting the drivers for energy storage adoption in Japan, of which he said there are two: increasing renewable energy generation and increasing demand for electricity.
With the grid’s share of renewables and low-carbon energy, not including nuclear, at about 20% today, the government is seeking to get to 36-38% by 2030, and to 50% renewables by 2050, its net zero target year. There will also be a commensurate decrease in generation from coal, Kawashima said.
On the second point, electricity demand, it is well known that Japan’s population is ageing, and decreasing, and the government had forecast that demand for power would not increase significantly.
“So the government felt, this is very easy. Increase renewable energy, decrease energy from coal power supply, but it will still be okay, because of the total demand decreases, in this original scenario,” Kawashima said.
However, in May of this year, “the government changed their minds, because of AI, data centres, everything,” he said. “The government is forecasting right now that demand will be increasing more than 35-50% to 2050,” and has identified energy storage as a key technology to enable better balancing of supply and demand.
“One of the key things that we see in terms of more renewables coming in, we’re seeing in many markets around the world, that creates other difficulties in the grid, in the market and batteries can solve a lot of that,” said Ross Bennett, of German state-owned bank NORD/LB.
More variability in generation between different times of day requires shifting energy to better meet morning and evening demand peaks, while more uncertainty in generation output means a greater need for backup.
Kyushu, the furthest south of Japan’s three main populated islands, is already seeing about 10% of renewable generation economically curtailed, “wasted energy that’s not being dispatched,” Bennett said.
There is so far also only one ancillary services market for frequency response open to energy storage assets in Japan. Bennett said that is another area with high growth potential, while more projects with corporate power purchase agreements (PPAs) are coming into the Japanese market, leading to more trading in the spot market.
“With more trading in the spot market, there’s more volatility and opportunity for arbitrage players, which of course much further down the line is future opportunity for battery storage as well,” Bennett said.
‘Tough nut to crack’
While preventing curtailment is a valuable potential use case for energy storage in Japan as renewable generation increases, developing solar PV projects in Japan can have much longer lead times than in other markets, said Joost van Acht, managing director of ib vogt.
Van Acht is responsible for the European renewable energy developer’s development, investment and commercial transactions in the APAC region.
That includes setting the company’s strategy towards BESS development for both standalone ESS and batteries co-located with renewable generation.
“What makes it more complex for us in Japan is that generally the development cycles for renewables are quite long. So, we’re looking at the current grid situation, but then if you add the three, four years to develop a solar project, that situation might have changed quite considerably and that feeds then into your investment case,” van Acht said.
“We do find it quite challenging, but we do also see that if you can be smart about it, then you can combine batteries and solar together; there’s actually a very good opportunity to make some good money out of that.”
There’s a reason why Japan is a notoriously “tough nut to crack,” for foreign businesses, said Dr Mahdi Behrengrad ,of Singapore-headquartered Pacifico Energy, which currently has Japan’s largest operating solar PV portfolio.
“Japan’s sheer size and reputation, the establishment of the organisation and infrastructure, everything attracts lots of companies,” Behrengrad said, but noted that the number that succeed once there is relatively small.
That has been the case in solar, and in offshore wind too. One main reason for that is that renewable energy and storage markets are largely driven by auctions and subsidies, which are “notoriously single-buyer” procurements, “heavily impacted by regulations and which can evaporate in a year,” Behrengrad said.
“If you want to sell to government or government-affiliated or government-covered agencies, you should consider the risk that they change their mind, because it’s a hugely political debate.”
That presents a regulatory risk at the central government level, but what many foreign companies also fail to recognise are the regulatory risks at local level.
Behrengrad said that for one Pacifico project, land and grid connection had been secured, but when it came to construction, the local authority decided that it wanted to limit noise pollution from the asset to 40 decibels.
“I don’t say it’s rocket science, but all of this means money. It means cost, it means patience.”
Nick Morely of Eku Energy, which is the Australia-headquartered pureplay BESS developer set up by Macquarie Capital’s Green Investment Group to develop projects in territories including the UK, Australia and now Japan, echoed the sentiment that patience is key, as well as local partnerships.
“There are significant barriers, whether they be regulatory, as well as language and on the development front, the way that a lot of regulations are implemented, there’s a strong local layer as well,” Morely, who is Eku Energy’s technical lead for the APAC region, said.
“So, there’ll be federal laws, but then the prefectural governments are really the ones who are implementing them, and they have a certain amount of authority to make changes or require things above the federal regulation.”
On the technical side, getting grid connections for battery storage projects can be a challenge in many countries, but in Japan, the process can be even more complex than outside observers often appreciate, Morely said.
“In Japan, the primary challenge that we see is that the lead times to complete the grid connection are very significant and they’re also quite variable,” Morely said.
“You need to make an investment upfront, spend time with the utility and eventually you’ll get an answer back saying, ‘Okay, we need anywhere from two years to five or six years to make the connection ready for your project,’ and so if your capital isn’t patient, both to invest early to progress the grid connection with a significant risk attached, and patient to develop your project while you wait for that grid connection to be available, then you may find the market a bit unappealing.”
LTDA: ‘Not the only way to commercialise BESS projects in Japan’
One of two large-scale BESS units built and owned by Pacifico Energy, which were the first in the country to start wholesale market trading of energy. Image: Pacifico Energy.
The flipside is, of course, that both Japanese and overseas companies see the fundamental drivers for growth in the energy storage market, coupled with the government’s public announcements, as something it wants to support.
Much has been made of the recent first-ever low-carbon capacity market auction, called the ‘Long Term Decarbonization Auction’ (‘LTDA’).
This offered 20-year contracts underwritten by the government, and significant numbers of battery assets (1.1GW) and pumped hydro energy storage (557MW) were successful in the competitive solicitation process.
There are, however, “multiple pathways to commercialisation” of BESS in Japan, and the LTDA is not the only game in town, said Morley.
Eku recently announced what is thought to be a first-of-a-kind offtake agreement with utility company Tokyo Gas, for example.
“One of the things that’s attractive about Japan is that there are multiple commercialisation pathways there. It’s not completely dependent on the LTDA,” Morely said, although he qualified this statement by saying that strong policy support of the type offered through the auction is desirable, alongside the ability to pursue different business models.
Similarly, Behrengrad pointed out that Pacifico Energy was the first developer to put BESS assets into Japan’s wholesale electricity trading markets, one in the south in Kyushu, and one on the northern island of Hokkaido.
“We are the first company in Japan who built and now we own and operate fully merchant large-scale ESS in both Hokkaido and Kyushu, and it has been phenomenal. So that is the vibrancy that I like about Japan that you can do these things,” Behrengrad said.
Pacifico is also working to write up contracts that are “half-merchant, half-tolling,” and business models of this type may be what drives market activity in the long run, rather than single auction-led deployments.
The LTDA itself has two major issues, said Kawashima. The auction provided a “good signal” to the market that Japan is embracing energy storage, but the returns are too low, he said.
“It’s only 2% to 3% IRR, in this case, it’s better to put the money in the bank, to be frank,” Kawashima said.
Better money could be made from batteries if merchant revenue opportunities open up more, he said. Meanwhile, the risk is that the LTDA itself is not just a subsidy scheme to support energy storage.
Other low-carbon assets like nuclear, ammonia or hydrogen facilities could also participate, and with this year representing only the first staging of the LTDA, the scheme’s design could change year-on-year.
From a debt financier’s perspective, however, Bennett said the LTDA is an “attractive product,” characterised by long-term cashflow guarantees and a strong counterparty in the Japanese government.
“As we’ve seen in other auctions in Japan, the first round was very overbid, and the price or the ultimate outcome was perhaps sub-optimal for many developers,” Bennett said.
“But still, I think even with a low base IRR assumption, the cost of debt in Japan is very low,” he said, so if developers can combine their LTDA contracts with other revenue streams, it can improve their geared position.
Adapting to merchant revenues
Bennett agreed with Morely’s position that the LTDA is not the only way to commercialise a BESS asset in Japan, adding that it is also not the only way to get debt finance, as there are numerous potential large corporate offtakers in the country.
Hazelwood, a 150MW/150MWh BESS asset co-developed by Eku in Australia, where the company has benefitted from a variety of commercialisation options, Nick Morely said. Image: Eku Energy.
The banker made a comparison with the Australian market, which is starting to see more and more tolling agreements, as well as merchant business models, and projects or portfolios that blend both contracted and merchant revenues.
“There are various other ways that you can contract out the battery, of course. Many of these for Japan are maybe a little bit too soon at this stage, but I think all of that will likely come in time,” Bennett said.
“What we’ve seen in other markets is, this does usually come quickly, once it starts moving.”
Appetite for exposure to merchant risk will take time to develop in a market like Japan where renewable energy deployment and revenues have been so closely tied to a feed-in tariff (FiT) regime.
Behrengrad said that there are many companies in Japan that have the technical capability to deploy major infrastructure projects, and many companies with a strong background in energy trading in oil and gas.
The “comfort zone” provided by renewable energy FiTs, where the offtaker carries no credit risk and the prices are fixed, is not replicable in the more complex world of monetising the value of battery storage, he said.
Lessons from both those adjacent sectors can be readily applied to energy storage, but it’s the question of how to finance projects that needs to be answered, according to Behrengrad.
“I think the key difficulty that financiers have in Japan, when we talk about merchant exposure, is exactly as Mahdi was saying: to date, we haven’t needed to look at it,” Bennett said.
Bennett added that looking at the Australian market, an initial thirst for long-term contracted revenues has gradually given way to more merchant market exposure.
As contracts shortened from 20-year to 15-year and then 10-year in Australia, the “merchant tail,” the post-contract lifetime of the asset where there is freedom to play into merchant markets, increased.
“When you’re looking at a 15-year merchant tail, you obviously do a lot of merchant exposure analysis and there’s also more people playing in those markets as well from a trading perspective. So, there’s more liquidity, and there’s more comfort around that,” Bennett said.
“That’s also something that we’d see would be valuable in Japan to develop that merchant exposure, that merchant appetite.”
This article reported on a panel discussion from the Energy Storage Summit Asia 2024, hosted in Singapore earlier this month. Energy-Storage.news Premium subscribers can benefit from exclusive discounts to this and other events hosted by our publisher, Solar Media.
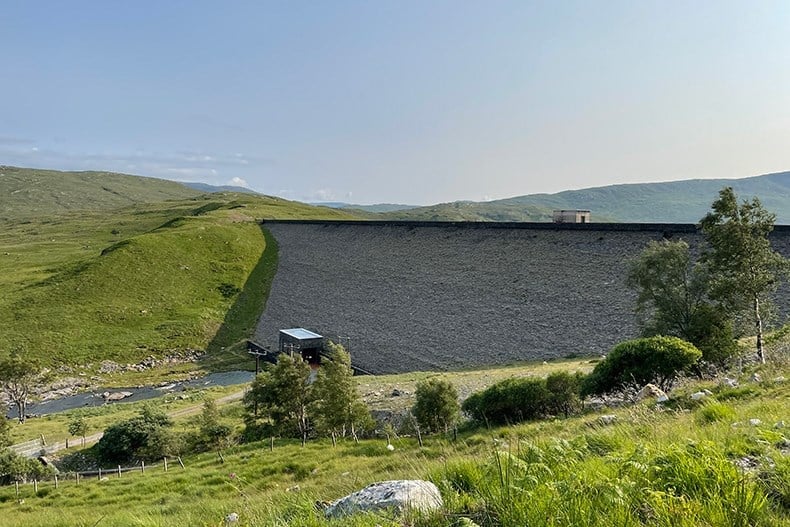
SSE Renewables plans 18GW/37GWh pumped hydro energy storage project in Scotland, UK
SSE Renewables, which is the renewable energy development arm of Scotland-headquartered multinational energy company SSE, announced its plans earlier this week (22 July).
If pursued, the project could produce around 37GWh of stored energy capacity, thus providing additional stability and flexibility to the GB grid. It would export energy for 20 hours at 1.8GW. A grid connection offer totalling 1.795GW has already been secured.
SSE confirmed the project could reach commercial operations in the mid-2030s, subject to reaching a final investment decision.
Gilkes Energy said the Fearna PHES project will complement the existing conventional hydro projects in the area and “represents the next chapter in Scotland’s rich hydropower heritage”.
Under the terms of the joint venture, Gilkes Energy will lead the project’s development under a development services agreement with SSE Renewables, leveraging the company’s experience in developing PHES projects in Scotland.
“The proposed Fearna project is a welcome addition to our development pipeline of pumped storage hydro projects, which also includes our proposal to develop what could be one of Britain’s biggest pumped storage schemes in 40-years at Coire Glas and our intention to convert our existing Sloy Power Station into a PHES facility,” Ross Turbet, head of investment management for hydro at SSE Renewables, said.
To read the full version of this story, visit Current.
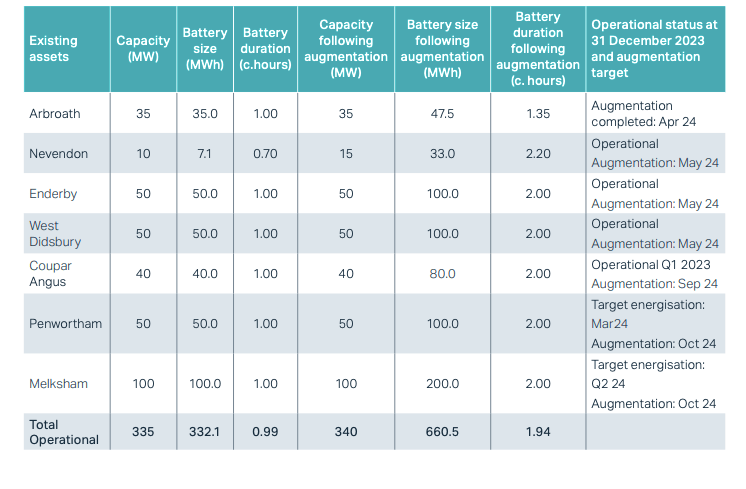
UK’s Gresham House discusses ongoing 328MWh BESS augmentation round
The firm’s New Energy assistant fund manager James Bustin was discussing its busy augmentation activities this year, with over 300MWh being added to its UK portfolio – activity which has come at the expense of its first international foray, as he explained.
“Going international has always been the plan, but this year we prioritised our cash focus on delivering duration upgrades in the UK. Augmentation provided the greatest returns right away, so we pulled away from that initial project in California, though we have others on the list,” Bustin said.
Between April and October this year, GRID is adding 328MWh of BESS capacity to seven existing projects, thereby increasing the average discharge duration of those projects from around one hour to around two hours.
The projects are Arbroath, Nevendon, Enderby, West Didsbury, Coupar Angus, Penwortham and Melksham.This table below, taken from the fund’s annual report, details the additions.
Image: Gresham House.
Bustin also discussed the company’s recent tolling deal with utility Octopus Energy, with those comments published in a separate article last week.
‘Using different parties does have challenges for augmentation’
The round of augmentations isn’t GRID’s first, after it turned most of its 30-minute duration sites – sometimes called 0.5C – to 1-hour ones, or 1C (1C meaning a 1:1 ratio between power and capacity) in 2018/2019.
“Each site has been designed with the idea of expanding, but there is never a pre-agreement with the provider. We’ve used two different battery types for the same project when augmenting and this is where our IP (intellectual property) comes in, having already done the augmentation five years ago which means we were familiar with the challenges,” Bustin said.
“The real advantage is around planning in advance, having the foundations laid for it. Having different providers for one project does have some challenges, but if you have experience augmenting it helps.”
“Not all providers are equal on this so we’re very careful about who we pick. Most parties should be able to deliver augmentation to some extent but we spent a lot of time choosing parties appropriately.”
He added that installing new BESS capacity can either involve adding that capacity ‘behind’ the inverter – what some might call DC augmentation – or ‘at’ the inverter – AC augmentation.
The latter potentially involves adding more more power conversion systems (PCS) alongside the additional BESS capacity which adds cost, while the former primarily involves shuffling existing BESS capacity behind inverters to maximise their usage.
The only of the seven projects above to have had its power capacity increased, which presumably required new PCS, was Enderby, going from being a 10MW/7.1MWh system to a 15MW/33MWh one.
System integrator Wärtsilä Energy Storage & Optimisation went into detail on augmentation in a technical paper for an edition of Solar Media’s PV Tech Power journal last year.
Bustin: “You can have different battery containers behind one inverter, if the control system is advanced enough. In our situation we’ve pooled like-for-like containers behind the inverter. In others we’ve done a sort of hybrid of the two types of augmentation.”
He also said that BESS solutions which provide both batteries and PCS integrated into one 20-foot container, increasingly popular so-called ‘AC blocks’, created a challenge for augmentation by limiting flexibility on design and structure. In other (admittedly very different) markets, like Chile, IPPs have said the opposite.
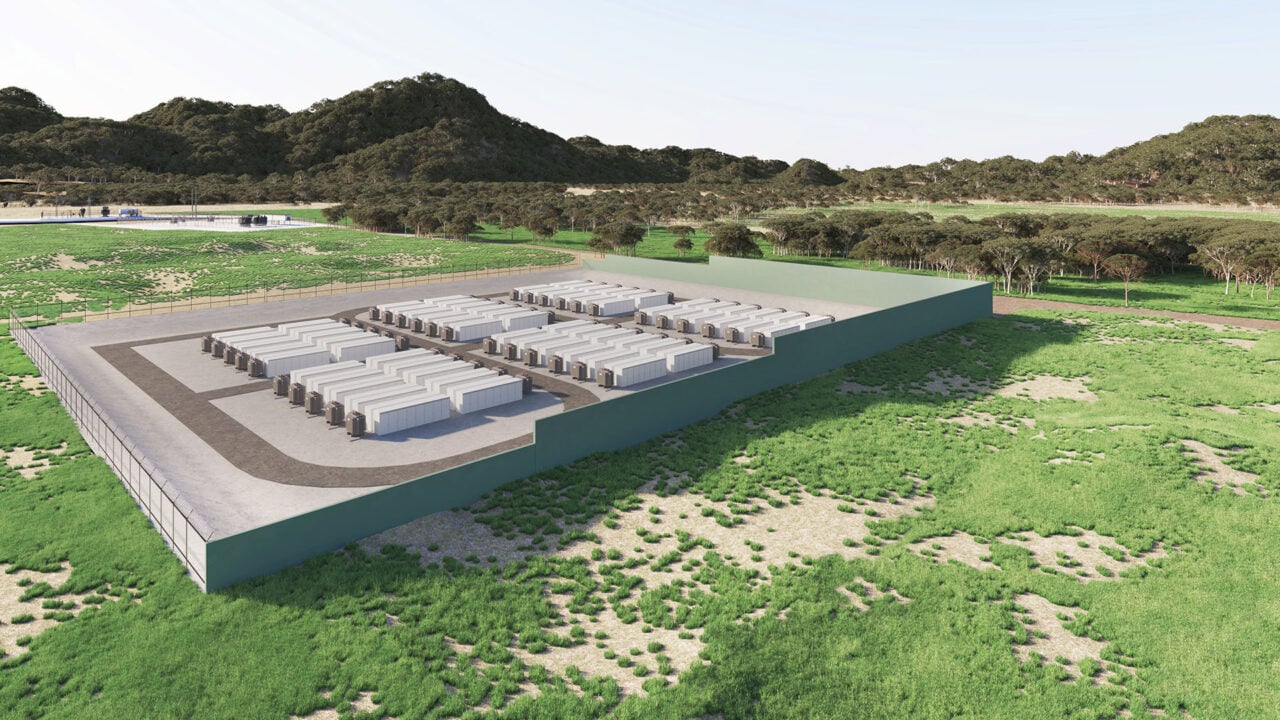
Eku Energy secures development approval for 500MWh BESS in the Australian Capital Territory
Securing approval of the development application is a key milestone on the project’s development. The application is a formal process for permission to build a new development in a designated area in ACT.
According to Eku Energy, the BESS is expected to enter the construction phase later this year and will be located in close proximity to the Williamsdale substation.
Eku Energy is responsible for developing, constructing, operating, and actively managing the Williamsdale BESS. Under an innovative revenue share agreement, it will share 50% of the net revenue with the Territory.
The Williamsdale BESS will also be registered to participate in the National Electricity Market (NEM), the main interconnected electricity network covering the east and south coasts of Australia.
Eku Energy partnered with the ACT government last year to develop, build, and operate the 250MW BESS. At the time, this was deemed a significant step in delivering the Big Canberra Battery ecosystem.
The initiative was first announced as part of the state’s 2020-2021 budget with AU$100 million (US$67 million) in funding pledged towards it. The government ran a procurement process for the grid-connected BESS which began in mid-2022 before its award to Eku just under a year later.
Eku Energy is an energy storage development platform that was launched through the Macquarie Asset Management-owned Green Investment Group (GIG) in late 2022
Eku Energy discusses business model variety
Eku Energy discussed how its Australian projects are developed under a variety of different business models, such as merchant, in an exclusive interview on Energy.Storage.news Premium last month (10 June).
Rachel Rundle, Eku Energy’s senior manager for policy and regulation in the APAC region, said that Eku Energy takes each project on a case-by-case basis, stating that it’s impossible to say what the commercial and revenue for schemes may look like. But the contribution the schemes could bring to the decarbonization of the country is unparalleled.
“We definitely see that with all the system challenges that we as a sector are aware of, through all these thermal plants coming out of the system, batteries are really well-placed to provide those services: whether it be system strength, whether it be synthetic inertia, voltage support, batteries are sort of that multi-tool asset,” Rundle said.
Most LDES projects set to be 8-hour systems, says California Energy Commission
The goal of the CEC report was to provide policymakers and stakeholders with a greater understanding of the role and costs associated with long-duration storage facilities within the state of California.
The report came shortly before the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) revealed on Friday (19 July) it has determined that the state bodies should conduct a centralised procurement of some 2GW of LDES, both multi-day and 12-hour-plus, alongside 7.6GW of offshore wind and 1GW of geothermal, covered in a separate article here.
‘Significant progress’ towards state net-zero goals
The report acknowledged that California had already made “significant progress” towards its net-zero goals, with 50% of electricity coming from renewable sources in 2023 with 28% coming from solar sources.
With the move away from dispatchable fossil-fuel resources such as gas-fired peaking plants, battery storage facilities will become increasingly important by providing electricity to the grid during times of critical need such as cloudy days and during the nighttime.
California is leading the way in the US in terms of energy storage deployment and already has over 10GW of storage capacity connected to the California Independent System Operator (CAISO) grid, as reported by Energy.Storage-News in April earlier this year.
However, the majority of currently operational storage facilities are only able to discharge for up to a maximum of four hours, meaning they aren’t able to supply electricity from sunset to sunrise when it’s often needed most, leading to the motivation behind LDES facilities.
With the demand for long-duration batteries increasing, companies specialising in LDES have been cropping up over the past decade with bespoke solutions such as Hydrostor with its patented advanced compressed air energy storage (A-CAES) system, Energy Vault with its gravitational storage technology and Form Energy with its iron-air battery.
Key findings: 8-hour duration facilities to make up majority of storage projects
The CEC report concluded that storage facilities with a range and mixture of durations from four to 100 hours would be needed to support the California grid, but facilities with an 8-hour duration would likely make up the largest proportion of LDES facilities. However, this would be heavily dependent on the US$/kW cost of energy and efficiency of the projects.
The report found that facilities with an 8-hour duration and an efficiency greater than 80% would be competitive with 4-hour facilities with a higher 85% efficiency for only a slightly lower US$/kW cost.
However, it found that when the efficiency of 8-hour facilities dropped to 50%, the US$/kW cost would need to be roughly half that of 4-hour duration facilities with an 85% efficiency in order to remain competitive within the market.
When considered on a “per watt” basis, the US$/kW cost targets to enter the market for 100-hour duration facilities are similar to the 8-hour storage facilities (for example, a 50MW/100-hour must have a similar cost to a 50MW/80-hour facility). However, if the efficiency of the 100-hour facility dropped from 80% to 50%, a 40% lower US$/kW cost would be needed in order for it to remain competitive.
Daytime EV charging could reduce cost of needed storage by US$1 billion
With the sale of new petrol-powered cars and light-trucks set to be banned in California from 2035, the report analysed the additional storage needed for 15 million EVs, averaging 40 miles/day, which results in a total load of 55 trillion watt-hours per year (TWh/y).
The report looked at three distinct charging scenarios: nighttime charging where EVs commence charging at midnight, unconstrained charging where a spontaneous pattern occurs with peak demand during the evening and finally daytime charging which incorporates a main peak demand during the morning but also a secondary one at midnight.
With vehicles charging during the daytime when renewable generating facilities such as wind and solar would be available, the CEC found that the daytime scenario would require the least storage capability, corresponding to cost differences compared to the nighttime scenario up to US$1 billion.
The full CEC report with all its findings can be found here.
California Energy Commission investments in LDES
The CEC has already made investments in LDES technology, including issuing Form Energy a US$30 million grant for the development of a 5MW/500MWh storage project at a substation owned by public utility PG&E in Mendocino County, California.
Form Energy claims that its iron-air batteries work on the principle of reversible rusting, with electrical energy being stored through the rusting of iron which can then be discharged for up to 100 hours.
Washington-based utility Puget Sound Energy (PGE) has also signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Form Energy for the deployment of an iron-air battery within its service territory, as reported in January 2024 by Energy.Storage-News. The pilot project is expected to have 10MW/1,000MWh of capacity and be online by the end of 2026.
US DOE’s Loan Programs Office to support Puerto Rico utility-scale solar PV and BESS
The projects themselves will comprise two utility-scale solar-plus-storage projects and two further standalone BESS projects located in the municipalities of Guayama and Salinas. Collectively, they are known as Project Maharu. The solar projects are projected to produce 460,000MWh of power annually.
The LPO said that the projects would help to support Puerto Rico’s grid reliability and energy security. In particular, it highlighted the role that BESS projects can play in maintaining power supply during extreme weather events; Puerto Rico’s power grid was severely affected by two hurricanes in 2017 and the country has since been hit with multiple earthquakes.
Project Maharu falls under numerous DOE and Federal government initiatives. It is part of the Biden administration’s Justice40 Initiative, which requires that 40% of the benefits of federal financing, including LPO investments, end up with “disadvantaged” communities. Most of Puerto Rico falls into this bracket.
The project will also be funded by the Energy Infrastructure Reinvestment (EIR), which was created as part of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) to support the replacement, repowering and repurposing of energy infrastructure which has either ceased operations or can be replaced to reduce carbon emissions.
The LPO said that the projects will help the replacement of Puerto Rico’s coal-based energy infrastructure, which the company has committed to ceasing entirely by 2028 before reaching a 100% renewable energy mix by 2050.
Energy-storage.news published an interview with the Director of the LPO, Jigar Shah, in October last year, which explored how the organisation funds renewable energy projects (Premium access). Shah said that the LPO supports companies that have met the commercial criteria to apply for debt financing support, rather than “picking” the companies to back. Shah has overseen something of a “resurrection” of the LPO, which was largely dormant during the Trump administration.
To read the full version of this story, visit PV Tech.
California eyes central procurement of 2GW of LDES to help scale novel technologies
The LDES portion is split between 1GW of multi-day energy storage, and another 1GW of energy storage with a discharge duration of 12 hours or more. The CPUC has said it wants resources that do not use lithium-ion batteries or pumped hydro energy storage (PHES) technologies, which are already commercialised and deployed at scale.
Other technologies are being targeted by the procurement by DWR because those technologies could help the state achieve its decarbonisation goals but are “not currently being procured by individual LSEs (load-serving entities, i.e. utilities) in significant enough amounts to achieve cost reductions,” the CPUC said.
California already has over 10GW of lithium-ion BESS online, primarily grid-scale, and that number will continue to grow substantially in the future. Project sizes are going up, with gigawatt-scale projects being progressed recently by NextEra Energy Resources and Avantus (both Premium access articles).
The determination comes after the Energy Research and Development Division of the California Energy Commission (CEC) issued a report highlighting the importance of energy storage resources with a discharge duration of eight hours or more recently.
DWR to act as central procurement body, resources for 2031-37 delivery
The CPUC will request the procurement of those resources, on behalf of the state’s electricity customers, by the Department of Water Resources (DWR), the state body responsible for the storage, management and regulation of the California’s water usage.
An ‘informal request’ may be sent to the DWR to initiate procurement within six months of the CPUC’s decision adoption. The CPUC’s schedule for solicitations would see the DWR, acting as a central procurement entity (CPE), launching solicitations for LDES in 2026 (as well as geothermal) with offshore wind the year after. The resources would then come online between 2031 and 2037.
See the CPUC’s decision document, in full, here. It clarified that the figures were maximum amounts, and that no procurement may happen if the prices offered by developers to the DWR were not cost-effective.
California is already providing US$380 million in grants for LDES projects, which it started paying out in November 2023.
Lithium-ion and PHES to be excluded
As part of the determination making process, the CPUC collected comments from a range of industry stakeholders including regulators and project developers.
Several were opposed to including lithium-ion in the procurement and, as such, the CPUC appears to have agreed, saying that both of the LDES procurement should not include lithium-ion batteries or PHES.
One of those was Hydrostor, the firm building large-scale projects in California and Australia using advanced compressed air energy storage (A-CAES) technology. Its comments were paraphrased in the CPUC’s decision document:
“Hydrostor is particularly concerned about technology neutrality in the LDES category, especially those technologies that are not lithium-ion batteries. In reply comments, Hydrostor points out that manyparties arguing in comments that LSEs can procure LDES on their own appear to be referring mainly or exclusively to lithium-ion batteries, and that this is not true for other diverse and emerging LDES technologies.”
The ‘100-hour, iron air battery’ company Form Energy also responded to the consultation, as did numerous utilities and developers and IPPs.
The UK government’s proposal to exclude lithium-ion from its LDES support scheme was also criticised by some stakeholders, primarily developers active with lithium-ion BESS project development (perhaps unsurprisingly).
Corporate funding for energy storage more than doubles year-on-year in first half of 2024
The sum raised across 64 corporate funding deals in total represented a 117% increase from the equivalent period of 2023 when US$7.1 billion was recorded from 59 deals.
It is short of the US$15.8 billion raised in H1 2022, although at the time it was noted by Mercom that the US$10.7 billion IPO by LG Energy Solution ‘distorted’ year-on-year comparisons.
It will be interesting to see how the rest of 2024 stacks up. 2022 went on to be an all-time high year with US$26 billion raised, up from US$17 billion in 2021. Although last year finished with a stronger second-half performance after a quiet start, the final total stood at US$19 billion in corporate funding for energy storage sector companies.
VC funding top five
Meanwhile, VC funding activity was dominated in dollar terms by money raised by lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery and energy storage companies.
Mercom’s top five VC deals for H1 2024 did, however, include three companies focused on non-lithium technologies: metal-hydrogen battery startup Enervenue, sodium-ion (Na-ion) company Natron Energy, and thermal heat and power storage company Antora Energy.
Company nameTechnologyVC deal amount (US$)Sila TechnologiesSilicon anodes for Li-ion batteries375 millionEnerVenueNickel-hydrogen batteries and storage systems308 millionNatron EnergySodium-ion batteries 189 millionAscend ElementsLithium battery recycler162 millionAntora EnergyThermal heat and power storage150 millionMercom’s Top Five VC funded deals for H1 2024
The top five represented a significant portion of the US$2.4 billion in VC funding raised from 28 deals during the period. This total was a 37% drop from H1 2023 when storage companies got US$3.8 billion from 43 deals.
In H1 2024, there were 16 debt and public market financing deals totalling US$13 billion, which was a massive 294% increase from US$3.3 billion from 16 deals during the same period of last year.
M&A activity into energy storage companies was up year-on-year, but there were fewer project-related M&A deals: there were 14 M&A transactions for companies in H1 2024 versus just eight in H1 2023, while there were 13 project M&A deals in the first six months of this year compared to 19 in H1 2023.
IPP Decci Group inaugurates largest BESS in Czech Republic
The project in Vraňany, Mělník, combines 30MW of BESS with another 22.4MW of gas generators to provide grid balancing services to the transmission system. Construction started in April last year and a May 2024 operation date was targeted.
Darina Merdassi, Decci’s director said the project would be able to provide the same balancing services as a 300MW lignite power plant, and that projects like it were key to moving away from coal, which still provides 60% of power in the Czech Republic (sometimes referred to as ‘Czechia’).
Specifically, Energy Nest will provide automatic frequency regulation backup (FCR), automatic activation power balance regulation backup (aFRR+) and manual activation power balance regulation backup (mFRR+), the announcement said. It will initially only bid in up to 30MW of its capacity, but this may increase to the full 52.4MW in future.
Merdassi added that the system could easily be expanded in future and that green hydrogen production is also being considered.
Technology company Siemens built the project while the main technology suppliers were turbine manufacturer Centrax and inverter company SMA. Local consulting firms Euroenergy, Nano Energies and OSC were also involved in the project while the Czech Institute of Informatics, Robotics and Cybernetics developed a customised control system.
Decci received a 750 CZK million (US$32 million) loan in November last year from Czech banks České spořitelny and Komerční Banka for the project.
It comes seven years after Energy-Storage.news reported on the first grid-scale lithium-ion BESS in the Czech Republic, deployed by system integrator Alfen.
See images and renders of Decci Group’s project below.
Images: Decci Group.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 2nd Energy Storage Summit Central Eastern Europe on 24-25 September this year in Warsaw, Poland. This event will bring together the region’s leading investors, policymakers, developers, utilities, energy buyers and service providers all in one place, as the region readies itself for storage to take off. Visit the official site for more info.